Company Details
toyota
31,153
2,230,806
3361
global.toyota
0
TOY_1082022
In-progress

Toyota Motor Corporation Company CyberSecurity Posture
global.toyotaToyota Motor Corporation is a global automotive industry leader manufacturing vehicles in 27 countries or regions and marketing the company’s products in over 170 countries and regions. Founded in 1937 and headquartered in Toyota City, Japan, Toyota Motor Corporation employs nearly 350,000 people globally.
Company Details
toyota
31,153
2,230,806
3361
global.toyota
0
TOY_1082022
In-progress
Between 700 and 749

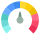 TMC Global Score (TPRM)
TMC Global Score (TPRM)XXXX

Description: A data breach revealed by Toyota Motor Corporation exposed information on more than 2 million consumers over ten years. A misconfigured database that was open to everyone without authentication was the source of the data breach. The security breach impacted customers who used the company’s T-Connect G-Link, G-Link Lite, or G-BOOK services. Exposed records include customer names, credit card data, and phone numbers have not been compromised as they weren’t stored in the exposed database.
Description: Japanese automaker Toyota had to suspend its domestic factory operations after Kojima Industries, which supplies the plastic parts and electronic components to the company was targeted in a cyber attack. The attack resulted in a halt at its 14 plants in Japan which contribute about a third of its global production.
Description: Toyota was listed among over 50 global corporations targeted in a large-scale data theft campaign by the **Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters** group. The attackers exploited vulnerabilities in **Salesforce customer environments**, including weak OAuth protections and inadequate two-factor authentication, to exfiltrate **multiple terabytes of sensitive data**. The stolen records reportedly include **personally identifiable information (PII)** such as driver’s licenses, dates of birth, social security numbers, and other regulated fields. The group claims to hold **strategic corporate data** that could undermine Toyota’s market position, with sample leaks ranging from single-digit gigabytes to hundreds of gigabytes per victim. The threat actors set a **public disclosure deadline (October 10, 2025)**, demanding ransom payments under the threat of full data exposure. While Toyota has not confirmed the authenticity of the leaked samples, the breach aligns with a year-long campaign targeting high-profile enterprises across industries, raising severe compliance risks under **GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations**. The attack’s scale and the nature of the exfiltrated data suggest **profound operational, financial, and reputational consequences** for the automaker.
Description: Toyota Motor Corp. disclosed the discovery of yet another data breach, this time involving the leakage of 260,000 automobile owners' personal data over the course of two improperly setup cloud services. After revealing earlier in the month that the data of 2.15 million customers was accessible to anyone online for more than 10 years, the automaker looked into the cloud features and made this revelation. It should be assumed that all of this data was repeatedly hacked given how long it was available. Information about customers, including names, contact information (including phone and email addresses), and vehicle identification numbers, may have been externally available.
Description: Toyota was affected by a cyber-attack by an unauthorized access from a third party. Toyota subsidiary Auto Parts Manufacturing Mississippi has revealed a ransomware attack where some financial and customer data was stolen and leaked, which is a strategy used by ransomware vendors to increase the leverage with which they can demand payment.
Description: In June 2025, the Qilin ransomware group targeted an automotive manufacturer, highlighting a strategic shift toward high-impact targets. The attack methodology demonstrated expertise in identifying vulnerabilities within interconnected systems, focusing on entities critical to global supply chains. This sophisticated approach compromised essential nodes, triggering widespread operational disruptions. The group's technical prowess, incorporating advanced reconnaissance and persistent access mechanisms, ensured prolonged network infiltration, rendering initial detection and remediation attempts ineffective.


Toyota Motor Corporation has 233.33% more incidents than the average of same-industry companies with at least one recorded incident.
Toyota Motor Corporation has 159.74% more incidents than the average of all companies with at least one recorded incident.
Toyota Motor Corporation reported 2 incidents this year: 1 cyber attacks, 1 ransomware, 0 vulnerabilities, 0 data breaches, compared to industry peers with at least 1 incident.
TMC cyber incidents detection timeline including parent company and subsidiaries

Toyota Motor Corporation is a global automotive industry leader manufacturing vehicles in 27 countries or regions and marketing the company’s products in over 170 countries and regions. Founded in 1937 and headquartered in Toyota City, Japan, Toyota Motor Corporation employs nearly 350,000 people globally.


Company profile GRAMMER AG, which has its head office in Ursensollen, specializes in the development and production of complex components and systems for automotive interiors as well as suspension driver and passenger seats for onroad and offroad vehicles. In the Automotive product area, the Company

Adient (NYSE: ADNT) is a global leader in automotive seating. With 70,000+ employees in 29 countries, Adient operates more than 200 manufacturing/assembly plants worldwide. We produce and deliver automotive seating for all major OEMs. From complete seating systems to individual foam, trim and metal
With its four brands BMW, MINI, Rolls-Royce and BMW Motorrad, the BMW Group is the world’s leading pre-mium manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles and also provides premium financial services. The BMW Group production network comprises over 30 production sites worldwide; the company has a globa

PACCAR is a global technology leader in the design, manufacture and customer support of premium light-, medium- and heavy-duty trucks under the Kenworth, Peterbilt and DAF nameplates. PACCAR also designs and manufactures advanced diesel engines, provides financial services, information technology, a
Iveco Group N.V. (MI: IVG) is the home of unique people and brands that power your business and mission to advance a more sustainable society. The seven brands are each a major force in its specific business: IVECO, a pioneering commercial vehicles brand that designs, manufactures, and markets heavy
Nissan Motor Corporation is a global car manufacturer that sells a full line of vehicles under the Nissan and INFINITI brands. Nissan’s global headquarters in Yokohama, Japan, manages operations in four regions: Japan-ASEAN, China, Americas, and AMIEO (Africa, Middle East, India, Europe & Oceania).

General Motors’ vision is to create a world with Zero Crashes, Zero Emissions and Zero Congestion, and we have committed ourselves to leading the way toward this future. Today, we are in the midst of a transportation revolution, and we have the ambition, the talent and the technology to realize the

Hero MotoCorp Ltd. (Formerly Hero Honda Motors Ltd.) is the world's largest manufacturer of two - wheelers, based in India. In 2001, the company achieved the coveted position of being the largest two-wheeler manufacturing company in India and also, the 'World No.1' two-wheeler company in terms of un
Doing something different is never easy. It requires courage, optimism and grit. Core to our mission is building a team of adventurous individuals determined to make a positive impact on the world. This means challenging ourselves constantly. Stretching beyond the bounds of conventional thinking. Re
.png)
Mihoko Matsubara of NTT shares insights on recent cyberattacks and how global firms can improve defences amid rising ransomware and supply...
On October 3, 2025, Hackread.com published an in-depth report in which hackers claimed to have stolen 989 million records from 39 major...
In a significant cybersecurity breach that has shaken the travel and business sectors, Qantas Airways has confirmed that sensitive data from...
The cybersecurity landscape has been shaken by the emergence of Trinity of Chaos, a sophisticated ransomware collective that has launched a...
Australia's largest telco is the latest company to become embroiled in a wide-ranging extortion hack on software company Salesforce,...
A cybercrime collective known as Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters has launched a new data leak site on the dark web, claiming it holds nearly one...
The hacking group claims to have stolen about a billion records from companies, including FedEx, Qantas, and TransUnion, who store their...
Toyota Motor Corporation, a global leader in automotive manufacturing. Known for its relentless focus on quality, safety, and innovation,...
Storm-2603, a China-linked cyber-espionage group, exploited a zero-day in Microsoft SharePoint Server (Toolshell) and by July 23 had...

Explore insights on cybersecurity incidents, risk posture, and Rankiteo's assessments.
The official website of Toyota Motor Corporation is http://www.toyota-global.com/.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation’s AI-generated cybersecurity score is 717, reflecting their Moderate security posture.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation currently holds 0 security badges, indicating that no recognized compliance certifications are currently verified for the organization.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation is not certified under SOC 2 Type 1.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation does not hold a SOC 2 Type 2 certification.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation is not listed as GDPR compliant.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation does not currently maintain PCI DSS compliance.
According to Rankiteo, Toyota Motor Corporation is not compliant with HIPAA regulations.
According to Rankiteo,Toyota Motor Corporation is not certified under ISO 27001, indicating the absence of a formally recognized information security management framework.
Toyota Motor Corporation operates primarily in the Motor Vehicle Manufacturing industry.
Toyota Motor Corporation employs approximately 31,153 people worldwide.
Toyota Motor Corporation presently has no subsidiaries across any sectors.
Toyota Motor Corporation’s official LinkedIn profile has approximately 2,230,806 followers.
Toyota Motor Corporation is classified under the NAICS code 3361, which corresponds to Motor Vehicle Manufacturing.
No, Toyota Motor Corporation does not have a profile on Crunchbase.
Yes, Toyota Motor Corporation maintains an official LinkedIn profile, which is actively utilized for branding and talent engagement, which can be accessed here: https://www.linkedin.com/company/toyota.
As of December 11, 2025, Rankiteo reports that Toyota Motor Corporation has experienced 6 cybersecurity incidents.
Toyota Motor Corporation has an estimated 12,645 peer or competitor companies worldwide.
Incident Types: The types of cybersecurity incidents that have occurred include Cyber Attack, Data Leak, Ransomware and Breach.
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through an communication strategy with threat actors demand victims verify corporate emails to establish real-time communication for ransom negotiations...
Title: Cyber Attack on Toyota Supplier Kojima Industries
Description: Japanese automaker Toyota had to suspend its domestic factory operations after Kojima Industries, which supplies the plastic parts and electronic components to the company was targeted in a cyber attack. The attack resulted in a halt at its 14 plants in Japan which contribute about a third of its global production.
Type: Cyber Attack
Title: Toyota Ransomware Attack
Description: Toyota subsidiary Auto Parts Manufacturing Mississippi was affected by a ransomware attack where some financial and customer data was stolen and leaked.
Type: Ransomware
Attack Vector: Unauthorized access from a third party
Motivation: Financial gain
Title: Toyota Data Breach
Description: A data breach revealed by Toyota Motor Corporation exposed information on more than 2 million consumers over ten years. A misconfigured database that was open to everyone without authentication was the source of the data breach. The security breach impacted customers who used the company’s T-Connect G-Link, G-Link Lite, or G-BOOK services. Exposed records include customer names, credit card data, and phone numbers have not been compromised as they weren’t stored in the exposed database.
Type: Data Breach
Attack Vector: Misconfigured Database
Vulnerability Exploited: Open database without authentication
Title: Toyota Data Breach Involving 260,000 Automobile Owners' Personal Data
Description: Toyota Motor Corp. disclosed the discovery of yet another data breach, this time involving the leakage of 260,000 automobile owners' personal data over the course of two improperly setup cloud services. After revealing earlier in the month that the data of 2.15 million customers was accessible to anyone online for more than 10 years, the automaker looked into the cloud features and made this revelation. It should be assumed that all of this data was repeatedly hacked given how long it was available. Information about customers, including names, contact information (including phone and email addresses), and vehicle identification numbers, may have been externally available.
Type: Data Breach
Attack Vector: Improperly setup cloud services
Vulnerability Exploited: Cloud misconfiguration
Title: Qilin Ransomware Group's Surge in High-Value Targeted Attacks
Description: The Qilin ransomware group emerged as a dominant threat actor in June 2025, orchestrating an unprecedented surge in high-value targeted attacks across multiple sectors and geographical regions. This escalation represents a fundamental transformation in ransomware operations, moving beyond traditional financial motivations to encompass strategic and political objectives that threaten global infrastructure stability.
Date Detected: June 2025
Type: Ransomware
Attack Vector: Vulnerabilities within interconnected systemsAdvanced reconnaissance techniquesPersistent access mechanisms
Threat Actor: Qilin Ransomware Group
Motivation: Strategic objectivesPolitical objectivesReputation damage
Title: Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters Data-Theft Campaign Exploiting Salesforce Products
Description: The hacking and cybercrime collective Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters published a dedicated online portal claiming responsibility for a wide-scale data-theft campaign involving the exploitation of Salesforce products. The group posted samples tied to over 50 corporate victims, including major global brands across automotive, retail, transportation, hospitality, and cloud SaaS. They claim to have exfiltrated 'multiple TBs' of data and 'near 1 billion records' containing sensitive PII (e.g., driver's licenses, SSNs, dates of birth). The group set a public disclosure deadline of October 10, 2025, threatening full data release unless victims comply. The campaign allegedly exploited weak OAuth protections, poor 2FA enforcement, and third-party integrations (e.g., Salesloft’s Drift/Drift). Victims span jurisdictions with strict privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA), and some have previously disclosed Salesforce-related breaches, while others were newly disclosed. The actors demand ransom payments in exchange for data deletion and offer litigation support to pressure compliance.
Type: Data Breach
Attack Vector: Exploitation of Salesforce Customer InstancesOAuth AbuseThird-Party App Compromises (e.g., Salesloft’s Drift/Drift)VPN Masking for ExfiltrationWeak 2FA Enforcement
Vulnerability Exploited: Poor OAuth ProtectionsLack of Multi-Factor Authentication (2FA) EnforcementThird-Party Integration Vulnerabilities (Salesforce-connected apps)
Threat Actor: Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters
Motivation: Financial Gain (Ransom Extortion)Data Theft for Resale/LeveragePublic Disclosure ThreatsLitigation Support as Pressure Tactic
Common Attack Types: The most common types of attacks the company has faced is Cyber Attack.
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through Salesforce Customer InstancesThird-Party Integrations (e.g. and Salesloft’s Drift/Drift)OAuth Abuse.

Systems Affected: 14 plants in Japan
Downtime: ['halt at its 14 plants in Japan']
Operational Impact: suspension of domestic factory operations

Data Compromised: Financial data, Customer data

Data Compromised: Customer names
Systems Affected: T-Connect G-LinkG-Link LiteG-BOOK

Data Compromised: Names, Contact information (phone and email addresses), Vehicle identification numbers

Systems Affected: Automotive manufacturersEnergy companiesMedical institutionsGovernment agenciesEntertainment venuesCritical infrastructure providers
Operational Impact: Widespread operational disruptions
Brand Reputation Impact: Reputation damage tactics

Data Compromised: Sensitive pii (driver’s licenses, social security numbers, dates of birth), Strategic corporate data (market position compromise risk), Raw records (regulated fields)
Systems Affected: Salesforce Customer InstancesThird-Party Integrations (e.g., Salesloft’s Drift/Drift)OAuth-Connected Apps
Brand Reputation Impact: High (Public Disclosure Threat, Global Brands Affected)
Legal Liabilities: Potential GDPR/CCPA/HIPAA ViolationsLitigation Risks (Threat Actors Offer Support to Pressure Compliance)
Identity Theft Risk: High (PII Exfiltrated)
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are Financial Data, Customer Data, , Customer Names, , Names, Contact Information (Phone And Email Addresses), Vehicle Identification Numbers, , Pii (Driver’S Licenses, Ssns, Dates Of Birth), Strategic Corporate Data, Raw Regulated Records and .

Entity Name: Toyota
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Automotive
Location: Japan

Entity Name: Kojima Industries
Entity Type: Supplier
Industry: Automotive
Location: Japan

Entity Name: Auto Parts Manufacturing Mississippi
Entity Type: Subsidiary
Industry: Automotive
Location: Mississippi

Entity Name: Toyota Motor Corporation
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Automotive
Customers Affected: 2000000

Entity Name: Toyota Motor Corp.
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Automotive
Customers Affected: 260000

Industry: Automotive, Energy, Medical, Government, Entertainment, Critical Infrastructure
Location: United StatesColombiaUnited Arab EmiratesFrance

Entity Name: Toyota
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Automotive
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: FedEx
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Transportation/Logistics
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Disney/Hulu
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Entertainment/Hospitality
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: UPS
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Transportation/Logistics
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Aeroméxico
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Aviation/Transportation
Location: Mexico/Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Home Depot
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Retail
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Marriott
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Hospitality
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Walgreens
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Retail/Pharmacy
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Stellantis
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Automotive
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Qantas
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Aviation/Transportation
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Google AdSense
Entity Type: Subsidiary
Industry: Technology/Advertising
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: Cisco
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Technology/Networking
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Entity Name: TransUnion
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Financial Services/Credit Reporting
Location: Global
Size: Large Enterprise

Communication Strategy: Threat actors demand victims verify corporate emails to establish real-time communication for ransom negotiations.

Type of Data Compromised: Financial data, Customer data

Type of Data Compromised: Customer names
Number of Records Exposed: 2000000
Personally Identifiable Information: customer names

Type of Data Compromised: Names, Contact information (phone and email addresses), Vehicle identification numbers
Number of Records Exposed: 260000
Personally Identifiable Information: NamesContact information (phone and email addresses)Vehicle identification numbers

Type of Data Compromised: Pii (driver’s licenses, ssns, dates of birth), Strategic corporate data, Raw regulated records
Number of Records Exposed: Near 1 billion
Sensitivity of Data: High (PII, Regulated Fields, Market-Sensitive Data)
Data Exfiltration: Confirmed (Multiple TBs Exfiltrated)
Personally Identifiable Information: Driver’s LicensesSocial Security NumbersDates of Birth

Data Exfiltration: True

Ransomware Strain: Qilin

Ransom Demanded: Implied (Payment for Data Deletion)
Data Exfiltration: Yes (Primary Tactics)

Regulations Violated: Potential GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), HIPAA (Healthcare Data, if applicable),
Legal Actions: Threat Actors Offer Litigation Support to Pressure Compliance
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The company ensures compliance with regulatory requirements through Threat Actors Offer Litigation Support to Pressure Compliance.

Source: ANY.RUN

Source: CyberInsider
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at and Source: ANY.RUN, and Source: CyberInsider.

Investigation Status: Ongoing (No Victim Confirmation of Leaked Data Authenticity as of Reporting)
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through Threat actors demand victims verify corporate emails to establish real-time communication for ransom negotiations..

High Value Targets: Government Agencies, Global Brand Companies, Automotive Manufacturers, Energy Companies, Medical Institutions,
Data Sold on Dark Web: Government Agencies, Global Brand Companies, Automotive Manufacturers, Energy Companies, Medical Institutions,

Entry Point: Salesforce Customer Instances, Third-Party Integrations (E.G., Salesloft’S Drift/Drift), Oauth Abuse,
Reconnaissance Period: Over 1 Year (Campaign Spanning >12 Months)
High Value Targets: Pii Databases, Strategic Corporate Data,
Data Sold on Dark Web: Pii Databases, Strategic Corporate Data,

Root Causes: Weak Oauth Protections, Poor 2Fa Enforcement, Third-Party Integration Vulnerabilities, Vpn Exfiltration Masking,
Last Ransom Demanded: The amount of the last ransom demanded was Implied (Payment for Data Deletion).
Last Attacking Group: The attacking group in the last incident were an Qilin Ransomware Group and Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters.
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on June 2025.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident were financial data, customer data, , customer names, , Names, Contact information (phone and email addresses), Vehicle identification numbers, , Sensitive PII (Driver’s Licenses, Social Security Numbers, Dates of Birth), Strategic Corporate Data (Market Position Compromise Risk), Raw Records (Regulated Fields) and .
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident were 14 plants in Japan and T-Connect G-LinkG-Link LiteG-BOOK and Automotive manufacturersEnergy companiesMedical institutionsGovernment agenciesEntertainment venuesCritical infrastructure providers and Salesforce Customer InstancesThird-Party Integrations (e.g., Salesloft’s Drift/Drift)OAuth-Connected Apps.
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach were Sensitive PII (Driver’s Licenses, Social Security Numbers, Dates of Birth), financial data, customer names, Contact information (phone and email addresses), Names, Strategic Corporate Data (Market Position Compromise Risk), Raw Records (Regulated Fields), customer data and Vehicle identification numbers.
Number of Records Exposed in Most Significant Breach: The number of records exposed in the most significant breach was 1.0B.
Highest Ransom Demanded: The highest ransom demanded in a ransomware incident was Implied (Payment for Data Deletion).
Most Significant Legal Action: The most significant legal action taken for a regulatory violation was Threat Actors Offer Litigation Support to Pressure Compliance.
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident are ANY.RUN and CyberInsider.
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is Ongoing (No Victim Confirmation of Leaked Data Authenticity as of Reporting).
Most Recent Reconnaissance Period: The most recent reconnaissance period for an incident was Over 1 Year (Campaign Spanning >12 Months).
.png)
FreePBX Endpoint Manager is a module for managing telephony endpoints in FreePBX systems. Versions prior to 16.0.96 and 17.0.1 through 17.0.9 have a weak default password. By default, this is a 6 digit numeric value which can be brute forced. (This is the app_password parameter). Depending on local configuration, this password could be the extension, voicemail, user manager, DPMA or EPM phone admin password. This issue is fixed in versions 16.0.96 and 17.0.10.
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. In versions 2.8.11 and below, the MySQLWriteTool executes arbitrary SQL provided by the caller using PDO::prepare() + execute() without semantic restrictions. This is consistent with the name (“write tool”), but in an LLM/agent context it becomes a high-risk capability: prompt injection or indirect prompt manipulation can cause execution of destructive queries such as DROP TABLE, TRUNCATE, DELETE, ALTER, or privilege-related statements (subject to DB permissions). Deployments that expose an agent with MySQLWriteTool enabled to untrusted input and/or run the tool with a DB user that has broad privileges are impacted. This issue is fixed in version 2.8.12.
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. Versions 2.8.11 and below use MySQLSelectTool, which is vulnerable to Read-Only Bypass. MySQLSelectTool is intended to be a read-only SQL tool (e.g., for LLM agent querying, however, validation based on the first keyword (e.g., SELECT) and a forbidden-keyword list does not block file-writing constructs such as INTO OUTFILE / INTO DUMPFILE. As a result, an attacker who can influence the tool input (e.g., via prompt injection through a public agent endpoint) may write arbitrary files to the DB server if the MySQL/MariaDB account has the FILE privilege and server configuration permits writes to a useful location (e.g., a web-accessible directory). This issue is fixed in version 2.8.12.
Okta Java Management SDK facilitates interactions with the Okta management API. In versions 11.0.0 through 20.0.0, race conditions may arise from concurrent requests using the ApiClient class. This could cause a status code or response header from one request’s response to influence another request’s response. This issue is fixed in version 20.0.1.
The Auth0 Next.js SDK is a library for implementing user authentication in Next.js applications. When using versions 4.11.0 through 4.11.2 and 4.12.0, simultaneous requests on the same client may result in improper lookups in the TokenRequestCache for the request results. This issue is fixed in versions 4.11.2 and 4.12.1.

Get company history
Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.
