Company Details
intel-corporation
0
3,957,112
3344
intel.com
0
INT_3325864
In-progress

Intel Corporation Company CyberSecurity Posture
intel.comOur mission is to shape the future of technology to help create a better future for the entire world, that’s the power of Intel Inside. With more ingenuity and creativity inside, our work is at the heart of countless innovations. From major breakthroughs to things that make everyday life better— they’re all powered by Intel technology. With a career at Intel, you can help make the future more wonderful for everyone.
Company Details
intel-corporation
0
3,957,112
3344
intel.com
0
INT_3325864
In-progress
Between 750 and 799

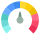 Intel Corporation Global Score (TPRM)
Intel Corporation Global Score (TPRM)XXXX

Description: A security researcher, Eaton Z, discovered critical vulnerabilities in Intel’s internal portals, including a business card login system that could be manipulated to bypass authentication. By exploiting weak verification mechanisms, the researcher accessed a **1GB data file** containing **personal details of over 270,000 Intel employees**, including names, roles, managers, addresses, and phone numbers. The breach extended beyond a single system, with **three additional Intel websites** (Product Hierarchy, Product Onboarding, and a supplier portal) found to have **hardcoded, easily decryptable credentials**, enabling unauthorized access. The exposed data poses severe risks, such as **identity theft, phishing, and social engineering attacks**, while also undermining Intel’s reputation in digital trust. Despite reporting the flaws in **October 2024**, Intel only patched them by **February 2025** and denied bug bounty compensation, citing program exclusions. The incident highlights how **basic application design oversights**—rather than sophisticated cyberattacks—can lead to large-scale internal data leaks, with potential long-term operational and security repercussions.
Description: Intel experienced a data breach that resulted in an online leak of 20GB of internal documents. Many files are marked confidential or restricted secret. The leaked files contained Intel intellectual property respective to the internal design of various chipsets. The files contained technical specs, product guides, and manuals for CPUs dating back to 2016.
Description: The links to the source code leak for the Intel UEFI BIOS of Alder Lake CPUs was recently posted by a Twitter user named 'freak'. The leak contained 5.97 GB of files, source code, private keys, change logs, and compilation tools, with the latest timestamp on the files being 9/30/22, likely to be the time when a hacker or insider copied the data. However it is still not confirmed that the source code was stolen during a cyberattack or leaked by an insider.
Description: The Iranian ransomware-as-a-service operation, Pay2Key.I2P, reemerged after a five-year hiatus, targeting organizations in the US and Israel. The group, linked to the Iranian government-backed Pioneer Kitten, has a history of targeting Israeli companies, including Intel's subsidiary Habana Labs. In late 2020, Pay2Key claimed to have stolen 53GB of data from Habana Labs, threatening to leak it. The group's updated ransomware now includes capabilities from Mimic ransomware, posing a significant threat to organizations' data security.
Description: A newly discovered class of vulnerabilities in Intel processors, termed Branch Predictor Race Conditions (BPRC), allows attackers to systematically extract sensitive data from the cache and random-access memory (RAM) of other users sharing the same hardware. Affecting all Intel processors released in the past six years-including those in consumer devices and cloud server infrastructure-the vulnerability exploits speculative execution technologies designed to accelerate computational performance. Researchers from ETH Zurich’s Computer Security Group (COMSEC) demonstrated that malicious actors could leverage BPRC to bypass privilege barriers at the processor level, achieving unauthorized readouts of memory contents at rates exceeding 5,000 bytes per second. This flaw poses acute risks for multi-tenant cloud environments, where shared hardware resources amplify the potential for cross-user data breaches. Speculative Execution and Its Inherent Security Trade-Offs Modern processors employ speculative execution to predict and precompute likely instructions, reducing latency in program execution. By anticipating branches in code execution paths, such as conditional statements, CPUs can maintain computational throughput even during delays caused by data fetches from slower memory systems. However, this performance optimization creates side channels that attackers can exploit. ETH Zurich’s Kaveh Razavi, head of COMSEC, notes that speculative technologies “fundamentally undermin
Description: A series of critical vulnerabilities across multiple internal Intel websites enabled the complete exfiltration of the company’s **global employee database** (270,000+ records) and unauthorized access to **confidential supplier information**, including NDAs. The flaws—stemming from **client-side authentication bypasses, hardcoded credentials (e.g., weak AES key '1234567890123456'), lack of server-side validation, and fabricated token acceptance (e.g., 'Not Autorized')**—were exploited via four distinct pathways. Key breaches included: - **Intel India’s business card ordering site**: Bypassed Azure login via JavaScript modification, exposing an unauthenticated API that returned a 1GB JSON file with **employee names, roles, managers, phone numbers, and mailbox addresses**. - **Product Hierarchy site**: Hardcoded, easily decrypted credentials granted backend access to the same employee database. - **Product Onboarding site**: Contained **hardcoded API keys and a GitHub personal access token**, risking further supply chain compromise. - **Supplier EHS IP Management System (SEIMS)**: Token validation bypass allowed **administrative access to supplier NDAs and IP data**. Intel remediated the vulnerabilities post-disclosure (October 2024), but the incident highlights systemic security oversights. While **no SSNs or salaries were exposed**, the **mass PII breach of employees and partners** poses severe reputational, operational, and compliance risks.


Intel Corporation has 12.36% more incidents than the average of same-industry companies with at least one recorded incident.
Intel Corporation has 29.87% more incidents than the average of all companies with at least one recorded incident.
Intel Corporation reported 1 incidents this year: 0 cyber attacks, 0 ransomware, 1 vulnerabilities, 0 data breaches, compared to industry peers with at least 1 incident.
Intel Corporation cyber incidents detection timeline including parent company and subsidiaries

Our mission is to shape the future of technology to help create a better future for the entire world, that’s the power of Intel Inside. With more ingenuity and creativity inside, our work is at the heart of countless innovations. From major breakthroughs to things that make everyday life better— they’re all powered by Intel technology. With a career at Intel, you can help make the future more wonderful for everyone.

Microchip Technology Inc. is a leading semiconductor supplier of smart, connected and secure embedded control solutions. Its easy-to-use development tools and comprehensive product portfolio enable customers to create optimal designs which reduce risk while lowering total system cost and time to mar
We anticipate tomorrow’s needs—navigating a changing world by bringing together technology's brightest minds to build game-changing solutions that propel us forward. NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NASDAQ: NXPI) is the trusted partner for innovative solutions in the automotive, industrial & IoT, mobile, an

We care deeply about transforming lives with AMD technology to enrich our industry, our communities, and the world. Our mission is to build great products that accelerate next-generation computing experiences – the building blocks for the data center, artificial intelligence, PCs, gaming and embedde
Micron is an industry leader in innovative memory and storage solutions transforming how the world uses information to enrich life for all. With a relentless focus on our customers, technology leadership, and manufacturing and operational excellence, Micron delivers a rich portfolio of high-performa
We are a global semiconductor company that designs, manufactures and sells analog and embedded processing chips for markets such as industrial, automotive, personal electronics, enterprise systems and communications equipment. At our core, we have a passion to create a better world by making electro

Lam Research Corp. (NASDAQ:LRCX) At Lam Research, we create equipment that drives technological advancements in the semiconductor industry. Our innovative solutions enable chipmakers to power progress in nearly all aspects of modern life, and it takes each member of our team to make it possible. A

Who are we? ASML is an innovation leader in the global semiconductor industry. We make machines that chipmakers use to mass produce microchips. Founded in 1984 in the Netherlands with just a handful of employees, we’ve now grown to over 40,000 employees, 143 nationalities and more than 60 locations
Renesas is an embedded semiconductor solution provider driven by its Purpose ‘To Make Our Lives Easier.’ As the industry’s leading expert in embedded processing with unmatched quality and system-level know-how, we have evolved to provide scalable and comprehensive semiconductor solutions for automot
Applied Materials is the leader in materials engineering solutions that are at the foundation of virtually every new semiconductor and advanced display in the world. The technology we create is essential to advancing AI and accelerating the commercialization of next-generation chips. At Applied, we
.png)
Intel is pursuing legal action against former software engineer Jinfeng Luo, who allegedly downloaded approximately 18000 confidential...
The Intel case underscores the ongoing risk of insider threats and the need for stronger data protection measures.
Intel, the leading computer chip maker, has filed a lawsuit seeking at least $250,000 in damages from a former software engineer,...
Intel is pursuing legal action against a former software engineer who the company claims downloaded thousands of confidential files shortly...
Intel has filed a federal lawsuit against a former employee accused of downloading of classified documents shortly after being terminated.
A former Intel software engineer who spent over a decade with the company allegedly stole several thousand documents, including confidential...
Dataminr, a New York-based company specializing in real-time threat intelligence, announced plans Tuesday to acquire ThreatConnect,...
Microsoft ( ($MSFT) ) has been popular among investors this week. Here is a recap of the key news on this stock. Microsoft is making waves...
Intel Capital, a business arm of Intel Corporation has made it official that it is investing in startups called Fortanix and Pliops to strengthen and secure...

Explore insights on cybersecurity incidents, risk posture, and Rankiteo's assessments.
The official website of Intel Corporation is http://www.intel.com.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation’s AI-generated cybersecurity score is 769, reflecting their Fair security posture.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation currently holds 0 security badges, indicating that no recognized compliance certifications are currently verified for the organization.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation is not certified under SOC 2 Type 1.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation does not hold a SOC 2 Type 2 certification.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation is not listed as GDPR compliant.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation does not currently maintain PCI DSS compliance.
According to Rankiteo, Intel Corporation is not compliant with HIPAA regulations.
According to Rankiteo,Intel Corporation is not certified under ISO 27001, indicating the absence of a formally recognized information security management framework.
Intel Corporation operates primarily in the Semiconductor Manufacturing industry.
Intel Corporation employs approximately 0 people worldwide.
Intel Corporation presently has no subsidiaries across any sectors.
Intel Corporation’s official LinkedIn profile has approximately 3,957,112 followers.
Intel Corporation is classified under the NAICS code 3344, which corresponds to Semiconductor and Other Electronic Component Manufacturing.
Yes, Intel Corporation has an official profile on Crunchbase, which can be accessed here: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/intel.
Yes, Intel Corporation maintains an official LinkedIn profile, which is actively utilized for branding and talent engagement, which can be accessed here: https://www.linkedin.com/company/intel-corporation.
As of December 11, 2025, Rankiteo reports that Intel Corporation has experienced 6 cybersecurity incidents.
Intel Corporation has an estimated 1,267 peer or competitor companies worldwide.
Incident Types: The types of cybersecurity incidents that have occurred include Vulnerability, Ransomware and Breach.
Total Financial Loss: The total financial loss from these incidents is estimated to be $4 million.
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through an third party assistance with morphisec, and incident response plan activated with yes (remediation completed within 90 days), and third party assistance with eaton works (researcher who disclosed vulnerabilities), and containment measures with patch for client-side authentication bypass, containment measures with removal of hardcoded credentials, containment measures with server-side validation implemented, containment measures with api token validation fixes, containment measures with typo correction in authorization checks ('not autorized'), and remediation measures with code reviews for internal web applications, remediation measures with security audits for authentication flows, remediation measures with encryption key rotation policies, and communication strategy with automated reply to researcher (no direct communication), and enhanced monitoring with likely implemented post-incident (not specified), and incident response plan activated with yes (patches applied by late february 2025), and containment measures with patching vulnerable portals, containment measures with removing hardcoded credentials, and communication strategy with limited (automated response to researcher; no public statement detailed in the report), and third party assistance with eth zurich’s computer security group (comsec), and network segmentation with recommended for cloud providers to mitigate cross-tenant risks, and enhanced monitoring with recommended for detecting anomalous memory access patterns..
Title: Intel UEFI BIOS Source Code Leak for Alder Lake CPUs
Description: The links to the source code leak for the Intel UEFI BIOS of Alder Lake CPUs was recently posted by a Twitter user named 'freak'. The leak contained 5.97 GB of files, source code, private keys, change logs, and compilation tools, with the latest timestamp on the files being 9/30/22, likely to be the time when a hacker or insider copied the data.
Type: Data Leak
Threat Actor: Unknown
Title: Intel Data Breach
Description: Intel experienced a data breach that resulted in an online leak of 20GB of internal documents. Many files are marked confidential or restricted secret. The leaked files contained Intel intellectual property respective to the internal design of various chipsets. The files contained technical specs, product guides, and manuals for CPUs dating back to 2016.
Type: Data Breach
Title: Iranian Ransomware-as-a-Service Operation Reemerges
Description: An Iranian ransomware-as-a-service operation with ties to a government-backed cyber crew has reemerged after a nearly five-year hiatus, and is offering would-be cybercriminals cash to infect organizations in the US and Israel.
Date Detected: 2025-01-01
Date Publicly Disclosed: 2025-06-23
Type: Ransomware-as-a-Service
Attack Vector: Malware
Threat Actor: Pay2Key.I2P
Motivation: Financial, Geopolitical
Title: Critical Vulnerabilities in Intel's Internal Websites Leading to Massive Data Exfiltration
Description: A series of critical vulnerabilities across multiple internal Intel websites allowed for the complete exfiltration of the company’s global employee database (270,000+ records) and unauthorized access to confidential supplier information. The flaws included client-side authentication bypasses, hardcoded credentials (with weak AES encryption), lack of server-side validation, and an unauthenticated API issuing valid access tokens. Four distinct pathways enabled unauthorized download of the entire employee database, including names, job roles, managers, phone numbers, and mailbox addresses. Confidential supplier data, including NDAs, was also exposed via administrative access gained through manipulated API responses. The vulnerabilities were responsibly disclosed on October 14, 2024, and remediated by Intel before the 90-day disclosure period ended.
Date Detected: 2024-10-14
Type: Data Breach
Attack Vector: Client-side Authentication Bypass (JavaScript modification)Hardcoded Credentials (weak AES encryption: key '1234567890123456')Lack of Server-Side ValidationUnauthenticated API Issuing Valid Access TokensFabricated Authorization Token ('Not Autorized' typo bypass)API Response Manipulation for Administrative Access
Vulnerability Exploited: CWE-287: Improper Authentication (Authentication Bypass)CWE-798: Use of Hard-coded CredentialsCWE-352: Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) (via API manipulation)CWE-601: URL Redirection to Untrusted Site (Open Redirect) (via token manipulation)CWE-319: Cleartext Transmission of Sensitive Information (weak AES encryption)CWE-20: Improper Input Validation (lack of server-side checks)
Threat Actor: Unknown (Responsible Disclosure by Eaton Works Researcher)
Motivation: ResearchResponsible Disclosure
Title: Intel Staff Records Leaked Through Login Flaws, Exposing Sensitive Company Information
Description: A single manipulated portal exposed over 270,000 Intel employee details. Hardcoded credentials on internal portals raised serious security concerns. Security researcher Eaton Z discovered a business card portal with a login system that could be easily manipulated, allowing unauthorized access to a 1GB file containing personal details of all 270,000 Intel employees, including names, roles, managers, addresses, and phone numbers. The vulnerabilities extended to three other internal portals, including 'Product Hierarchy,' 'Product Onboarding,' and a supplier login page, all of which contained hardcoded or easily bypassed credentials. Intel patched the flaws by late February 2025 after being notified in October 2024, but no bug bounty was awarded due to program exclusions.
Date Detected: 2024-10
Date Publicly Disclosed: 2025-02
Date Resolved: 2025-02
Type: Data Breach
Attack Vector: Authentication BypassHardcoded CredentialsInsecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR)
Vulnerability Exploited: Weak Login VerificationHardcoded Credentials in Internal PortalsImproper Access Controls
Threat Actor: Eaton Z (Security Researcher)
Motivation: Research/Disclosure (Ethical)
Title: Branch Predictor Race Conditions (BPRC) Vulnerability in Intel Processors
Description: A newly discovered class of vulnerabilities in Intel processors, termed Branch Predictor Race Conditions (BPRC), allows attackers to systematically extract sensitive data from the cache and random-access memory (RAM) of other users sharing the same hardware. Affecting all Intel processors released in the past six years—including those in consumer devices and cloud server infrastructure—the vulnerability exploits speculative execution technologies designed to accelerate computational performance. Researchers from ETH Zurich’s Computer Security Group (COMSEC) demonstrated that malicious actors could leverage BPRC to bypass privilege barriers at the processor level, achieving unauthorized readouts of memory contents at rates exceeding 5,000 bytes per second. This flaw poses acute risks for multi-tenant cloud environments, where shared hardware resources amplify the potential for cross-user data breaches.
Type: Hardware Vulnerability
Attack Vector: Local Privilege EscalationCross-Tenant Data Theft in Cloud EnvironmentsMemory Cache Exploitation
Vulnerability Exploited: Branch Predictor Race Conditions (BPRC) in Intel Processors (Speculative Execution Side Channel)
Motivation: Data TheftEspionageUnauthorized Access to Sensitive Information
Common Attack Types: The most common types of attacks the company has faced is Breach.
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through Russian and Chinese darknet forums and X.

Data Compromised: Source code, Private keys, Change logs, Compilation tools

Data Compromised: Intellectual property, Technical specs, Product guides, Manuals

Financial Loss: More than $4 million
Data Compromised: 53GB of data from Habana Labs

Data Compromised: Employee pii (270,000+ records): names, job roles, managers, phone numbers, mailbox addresses, Confidential supplier data: ndas, intellectual property details
Systems Affected: Intel India Business Card Ordering WebsiteProduct Hierarchy Management WebsiteProduct Onboarding Site (ARK database management)Supplier EHS IP Management System (SEIMS)
Operational Impact: Potential supply chain disruptionsInternal process reviews required
Brand Reputation Impact: High (massive PII breach for a tech giant)Erosion of trust among employees and suppliers
Legal Liabilities: Potential GDPR/CCPA violations (PII exposure)Contractual breaches with suppliers (NDA violations)
Identity Theft Risk: ['Moderate (no SSNs/salaries exposed, but PII could enable phishing/social engineering)']

Data Compromised: Employee records (270,000), Names, Roles, Manager details, Addresses, Phone numbers
Systems Affected: Business Card PortalProduct Hierarchy PortalProduct Onboarding PortalSupplier Login Page
Operational Impact: High (Potential for identity theft, phishing, and social engineering attacks due to exposed employee data)
Brand Reputation Impact: Moderate to High (Erosion of digital trust, especially for a company emphasizing cybersecurity)
Identity Theft Risk: High

Data Compromised: Memory contents, Cache data, Ram data (cross-tenant in cloud environments)
Systems Affected: Intel Processors (Last 6 Years)Consumer DevicesCloud Server InfrastructureMulti-Tenant Environments
Operational Impact: Potential for Cross-User Data BreachesPrivilege Escalation RisksCompromised Confidentiality in Shared Hardware
Brand Reputation Impact: Potential Erosion of Trust in Intel Hardware SecurityConcerns Over Cloud Security
Identity Theft Risk: ['High (if PII is stored in affected memory)']
Payment Information Risk: ['High (if payment data is processed on vulnerable systems)']
Average Financial Loss: The average financial loss per incident is $666.67 thousand.
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are Source Code, Private Keys, Change Logs, Compilation Tools, , Intellectual Property, Technical Specs, Product Guides, Manuals, , Corporate Data, Personally Identifiable Information (Pii), Corporate Hierarchy Data, Supplier Confidential Information (Ndas, Ip Details), , Personally Identifiable Information (Pii), Employee Records, , Memory Cache Data, Ram Contents, Potentially Sensitive User/Data Center Information and .

Entity Name: Habana Labs
Entity Type: Company
Industry: Technology
Location: Israel

Entity Name: Intel Corporation
Entity Type: Multinational Corporation
Industry: Semiconductors/Technology
Location: Global (HQ: Santa Clara, California, USA)
Size: ~131,000 employees (270,000+ records exposed, including contractors)
Customers Affected: None (internal systems; employees and suppliers impacted)

Entity Name: Intel India Employees
Entity Type: Subsidiary Workforce
Industry: Technology
Location: India

Entity Name: Intel Suppliers (via SEIMS)
Entity Type: Business Partners
Industry: Various (technology/supply chain)
Location: Global

Entity Name: Intel Corporation
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Semiconductors/Technology
Location: Santa Clara, California, USA
Size: Large (120,000+ employees globally, though 270,000 records exposed)

Entity Name: Intel Corporation
Entity Type: Hardware Manufacturer
Industry: Semiconductors/Technology
Location: Santa Clara, California, USA
Size: Large (Global)
Customers Affected: Consumers, Enterprise Clients, Cloud Service Providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), Data Centers

Entity Name: Cloud Service Providers (Multi-Tenant Environments)
Entity Type: Service Provider
Industry: Cloud Computing
Location: Global
Size: Varies (Large Scale)
Customers Affected: All customers using shared Intel-based infrastructure

Third Party Assistance: Morphisec

Incident Response Plan Activated: Yes (remediation completed within 90 days)
Third Party Assistance: Eaton Works (Researcher Who Disclosed Vulnerabilities).
Containment Measures: Patch for client-side authentication bypassRemoval of hardcoded credentialsServer-side validation implementedAPI token validation fixesTypo correction in authorization checks ('Not Autorized')
Remediation Measures: Code reviews for internal web applicationsSecurity audits for authentication flowsEncryption key rotation policies
Communication Strategy: Automated reply to researcher (no direct communication)
Enhanced Monitoring: Likely implemented post-incident (not specified)

Incident Response Plan Activated: Yes (Patches applied by late February 2025)
Containment Measures: Patching Vulnerable PortalsRemoving Hardcoded Credentials
Communication Strategy: Limited (Automated response to researcher; no public statement detailed in the report)

Third Party Assistance: Eth Zurich’S Computer Security Group (Comsec).
Network Segmentation: ['Recommended for cloud providers to mitigate cross-tenant risks']
Enhanced Monitoring: Recommended for detecting anomalous memory access patterns
Incident Response Plan: The company's incident response plan is described as Yes (remediation completed within 90 days), Yes (Patches applied by late February 2025).
Third-Party Assistance: The company involves third-party assistance in incident response through Morphisec, Eaton Works (researcher who disclosed vulnerabilities), , ETH Zurich’s Computer Security Group (COMSEC), .

Type of Data Compromised: Source code, Private keys, Change logs, Compilation tools
File Types Exposed: source codeprivate keyschange logscompilation tools

Type of Data Compromised: Intellectual property, Technical specs, Product guides, Manuals
Sensitivity of Data: ConfidentialRestricted Secret

Type of Data Compromised: Corporate Data
Data Exfiltration: 53GB of data from Habana Labs

Type of Data Compromised: Personally identifiable information (pii), Corporate hierarchy data, Supplier confidential information (ndas, ip details)
Number of Records Exposed: 270,000+ (employees and workers)
Sensitivity of Data: Moderate to High (PII + confidential business data)
Data Exfiltration: Yes (1 GB JSON file with global workforce data)
Data Encryption: ["Weak (AES with key '1234567890123456')"]
File Types Exposed: JSON (employee database)API responses (supplier data)
Personally Identifiable Information: NamesJob RolesManagersPhone NumbersMailbox Addresses

Type of Data Compromised: Personally identifiable information (pii), Employee records
Number of Records Exposed: 270,000
Sensitivity of Data: High (Includes names, roles, managers, addresses, phone numbers)
Data Exfiltration: Yes (1GB file downloaded by researcher)
Data Encryption: No (Data was accessible in plaintext)
File Types Exposed: Database Dump/Export (likely CSV or similar)
Personally Identifiable Information: Yes (Names, addresses, phone numbers, roles, manager details)

Type of Data Compromised: Memory cache data, Ram contents, Potentially sensitive user/data center information
Sensitivity of Data: High (depends on memory contents, e.g., encryption keys, passwords, PII)
Data Exfiltration: Demonstrated at 5,000+ bytes per second
Personally Identifiable Information: Potential (if stored in memory)
Prevention of Data Exfiltration: The company takes the following measures to prevent data exfiltration: Code reviews for internal web applications, Security audits for authentication flows, Encryption key rotation policies, .
Handling of PII Incidents: The company handles incidents involving personally identifiable information (PII) through by patch for client-side authentication bypass, removal of hardcoded credentials, server-side validation implemented, api token validation fixes, typo correction in authorization checks ('not autorized'), , patching vulnerable portals, removing hardcoded credentials and .

Ransom Paid: More than $4 million
Ransomware Strain: Pay2Key.I2P
Data Exfiltration: Yes

Regulations Violated: Potential GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), Sector-specific data protection laws,

Lessons Learned: The incident highlights the convergence of state-sponsored cyber warfare and global cybercrime.

Lessons Learned: Critical importance of server-side validation over client-side checks, Dangers of hardcoded credentials, especially with weak encryption, Need for rigorous API security (token validation, rate limiting), Typos in code (e.g., 'Not Autorized') can have severe security implications, Bug bounty scope limitations may discourage reporting of critical infrastructure flaws

Lessons Learned: Hardcoded credentials and weak authentication mechanisms can lead to large-scale data exposure even in tech-savvy organizations., Internal portals must undergo rigorous security testing, including authentication bypass scenarios., Bug bounty program exclusions may discourage ethical disclosures if researchers are not fairly compensated for valid findings., Automated responses to vulnerability reports may undermine trust in an organization’s commitment to security.

Lessons Learned: Speculative execution optimizations introduce fundamental security trade-offs that can be exploited via side channels., Hardware-level vulnerabilities can have cascading impacts across consumer, enterprise, and cloud environments., Multi-tenant cloud architectures require additional safeguards to prevent cross-user data leakage via hardware flaws.

Recommendations: American businesses should guard their networks against Iranian government-sponsored cyberattacks and 'low-level' digital intrusions by pro-Iran hacktivists.

Recommendations: Implement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosuresImplement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosuresImplement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosuresImplement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosuresImplement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosuresImplement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosuresImplement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosures

Recommendations: Conduct comprehensive audits of internal portals for hardcoded credentials and authentication flaws., Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all internal systems, especially those handling sensitive data., Expand bug bounty program scope to include critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities., Enhance communication protocols for vulnerability disclosures to ensure researchers feel acknowledged and valued., Regularly test for Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and similar access control vulnerabilities.Conduct comprehensive audits of internal portals for hardcoded credentials and authentication flaws., Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all internal systems, especially those handling sensitive data., Expand bug bounty program scope to include critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities., Enhance communication protocols for vulnerability disclosures to ensure researchers feel acknowledged and valued., Regularly test for Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and similar access control vulnerabilities.Conduct comprehensive audits of internal portals for hardcoded credentials and authentication flaws., Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all internal systems, especially those handling sensitive data., Expand bug bounty program scope to include critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities., Enhance communication protocols for vulnerability disclosures to ensure researchers feel acknowledged and valued., Regularly test for Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and similar access control vulnerabilities.Conduct comprehensive audits of internal portals for hardcoded credentials and authentication flaws., Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all internal systems, especially those handling sensitive data., Expand bug bounty program scope to include critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities., Enhance communication protocols for vulnerability disclosures to ensure researchers feel acknowledged and valued., Regularly test for Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and similar access control vulnerabilities.Conduct comprehensive audits of internal portals for hardcoded credentials and authentication flaws., Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all internal systems, especially those handling sensitive data., Expand bug bounty program scope to include critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities., Enhance communication protocols for vulnerability disclosures to ensure researchers feel acknowledged and valued., Regularly test for Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and similar access control vulnerabilities.

Recommendations: Intel should release microcode/firmware patches to mitigate BPRC exploits., Cloud providers should implement network segmentation and memory isolation techniques for shared hardware., Organizations should monitor for unusual memory access patterns indicative of speculative execution attacks., Long-term: Redesign speculative execution mechanisms to eliminate side-channel risks without sacrificing performance.Intel should release microcode/firmware patches to mitigate BPRC exploits., Cloud providers should implement network segmentation and memory isolation techniques for shared hardware., Organizations should monitor for unusual memory access patterns indicative of speculative execution attacks., Long-term: Redesign speculative execution mechanisms to eliminate side-channel risks without sacrificing performance.Intel should release microcode/firmware patches to mitigate BPRC exploits., Cloud providers should implement network segmentation and memory isolation techniques for shared hardware., Organizations should monitor for unusual memory access patterns indicative of speculative execution attacks., Long-term: Redesign speculative execution mechanisms to eliminate side-channel risks without sacrificing performance.Intel should release microcode/firmware patches to mitigate BPRC exploits., Cloud providers should implement network segmentation and memory isolation techniques for shared hardware., Organizations should monitor for unusual memory access patterns indicative of speculative execution attacks., Long-term: Redesign speculative execution mechanisms to eliminate side-channel risks without sacrificing performance.
Key Lessons Learned: The key lessons learned from past incidents are The incident highlights the convergence of state-sponsored cyber warfare and global cybercrime.Critical importance of server-side validation over client-side checks,Dangers of hardcoded credentials, especially with weak encryption,Need for rigorous API security (token validation, rate limiting),Typos in code (e.g., 'Not Autorized') can have severe security implications,Bug bounty scope limitations may discourage reporting of critical infrastructure flawsHardcoded credentials and weak authentication mechanisms can lead to large-scale data exposure even in tech-savvy organizations.,Internal portals must undergo rigorous security testing, including authentication bypass scenarios.,Bug bounty program exclusions may discourage ethical disclosures if researchers are not fairly compensated for valid findings.,Automated responses to vulnerability reports may undermine trust in an organization’s commitment to security.Speculative execution optimizations introduce fundamental security trade-offs that can be exploited via side channels.,Hardware-level vulnerabilities can have cascading impacts across consumer, enterprise, and cloud environments.,Multi-tenant cloud architectures require additional safeguards to prevent cross-user data leakage via hardware flaws.
Implemented Recommendations: The company has implemented the following recommendations to improve cybersecurity: American businesses should guard their networks against Iranian government-sponsored cyberattacks and 'low-level' digital intrusions by pro-Iran hacktivists..

Source: Twitter user 'freak'

Source: US Homeland Security

Source: Eaton Works Research (Vulnerability Disclosure)

Source: TechRadar Pro

Source: Eaton Z (Security Researcher Blog Post)

Source: ETH Zurich’s Computer Security Group (COMSEC)
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at and Source: Twitter user 'freak', and Source: MorphisecDate Accessed: 2025-06-23, and Source: US Homeland Security, and Source: Eaton Works Research (Vulnerability Disclosure), and Source: TechRadar Pro, and Source: Eaton Z (Security Researcher Blog Post), and Source: ETH Zurich’s Computer Security Group (COMSEC).

Investigation Status: Ongoing

Investigation Status: Completed (vulnerabilities remediated)

Investigation Status: Resolved (Flaws patched as of February 2025)

Investigation Status: Ongoing (Research Demonstrated by ETH Zurich; No Public Incidents Reported Yet)
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through Automated Reply To Researcher (No Direct Communication) and Limited (Automated response to researcher; no public statement detailed in the report).

Customer Advisories: Intel and cloud providers should issue advisories warning customers of potential risks and mitigation steps.
Advisories Provided: The company provides the following advisories to stakeholders and customers following an incident: were Intel And Cloud Providers Should Issue Advisories Warning Customers Of Potential Risks And Mitigation Steps. and .

Entry Point: Russian and Chinese darknet forums, X
High Value Targets: US and Israel
Data Sold on Dark Web: US and Israel

Root Causes: State-sponsored cyber warfare and financial incentives

Root Causes: Over-Reliance On Client-Side Security Controls, Lack Of Secure Coding Practices (Hardcoded Credentials, Weak Encryption), Inadequate Api Security (Unauthenticated Token Issuance, Lack Of Input Validation), Poor Secret Management (Exposed Github Pat, Api Keys), Insufficient Security Testing For Internal Applications,
Corrective Actions: Server-Side Validation Enforced, Hardcoded Credentials Removed/Replaced With Secure Alternatives, Api Security Hardened (Token Validation, Rate Limiting), Encryption Standards Updated, Bug Bounty Program Review Initiated,

Root Causes: Hardcoded Credentials In Multiple Internal Portals., Weak Authentication Mechanisms Allowing Bypass Via Manipulated Login Requests., Lack Of Proper Access Controls To Restrict Data Exposure., Inadequate Response To Vulnerability Disclosure, Potentially Discouraging Future Ethical Reporting.,
Corrective Actions: Patched Vulnerable Portals And Removed Hardcoded Credentials., Presumably Reviewed And Strengthened Authentication Processes (Though Not Explicitly Detailed).,

Root Causes: Inherent Security Flaws In Speculative Execution Implementations In Intel Processors., Lack Of Hardware-Level Isolation Between Tenants In Shared Environments., Performance Optimizations Prioritized Over Security In Cpu Design.,
Post-Incident Analysis Process: The company's process for conducting post-incident analysis is described as Morphisec, Eaton Works (Researcher Who Disclosed Vulnerabilities), , Likely Implemented Post-Incident (Not Specified), , Eth Zurich’S Computer Security Group (Comsec), , Recommended For Detecting Anomalous Memory Access Patterns, .
Corrective Actions Taken: The company has taken the following corrective actions based on post-incident analysis: Server-Side Validation Enforced, Hardcoded Credentials Removed/Replaced With Secure Alternatives, Api Security Hardened (Token Validation, Rate Limiting), Encryption Standards Updated, Bug Bounty Program Review Initiated, , Patched Vulnerable Portals And Removed Hardcoded Credentials., Presumably Reviewed And Strengthened Authentication Processes (Though Not Explicitly Detailed)., .
Ransom Payment History: The company has Paid ransoms in the past.
Last Attacking Group: The attacking group in the last incident were an Unknown, Pay2Key.I2P, Unknown (Responsible Disclosure by Eaton Works Researcher) and Eaton Z (Security Researcher).
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on 2025-01-01.
Most Recent Incident Publicly Disclosed: The most recent incident publicly disclosed was on 2025-02.
Most Recent Incident Resolved: The most recent incident resolved was on 2025-02.
Highest Financial Loss: The highest financial loss from an incident was More than $4 million.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident were source code, private keys, change logs, compilation tools, , Intellectual Property, Technical Specs, Product Guides, Manuals, , 53GB of data from Habana Labs, Employee PII (270,000+ records): names, job roles, managers, phone numbers, mailbox addresses, Confidential Supplier Data: NDAs, intellectual property details, , Employee Records (270,000), Names, Roles, Manager Details, Addresses, Phone Numbers, , Memory Contents, Cache Data, RAM Data (Cross-Tenant in Cloud Environments) and .
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident was Intel India Business Card Ordering WebsiteProduct Hierarchy Management WebsiteProduct Onboarding Site (ARK database management)Supplier EHS IP Management System (SEIMS) and Business Card PortalProduct Hierarchy PortalProduct Onboarding PortalSupplier Login Page and Intel Processors (Last 6 Years)Consumer DevicesCloud Server InfrastructureMulti-Tenant Environments.
Third-Party Assistance in Most Recent Incident: The third-party assistance involved in the most recent incident was Morphisec, eaton works (researcher who disclosed vulnerabilities), , eth zurich’s computer security group (comsec), .
Containment Measures in Most Recent Incident: The containment measures taken in the most recent incident were Patch for client-side authentication bypassRemoval of hardcoded credentialsServer-side validation implementedAPI token validation fixesTypo correction in authorization checks ('Not Autorized') and Patching Vulnerable PortalsRemoving Hardcoded Credentials.
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach were Manuals, Addresses, private keys, compilation tools, Names, Product Guides, Phone Numbers, Employee Records (270,000), Memory Contents, Confidential Supplier Data: NDAs, intellectual property details, RAM Data (Cross-Tenant in Cloud Environments), 53GB of data from Habana Labs, Technical Specs, Roles, Intellectual Property, Manager Details, change logs, source code, Employee PII (270,000+ records): names, job roles, managers, phone numbers, mailbox addresses and Cache Data.
Number of Records Exposed in Most Significant Breach: The number of records exposed in the most significant breach was 540.0K.
Highest Ransom Paid: The highest ransom paid in a ransomware incident was More than $4 million.
Most Significant Lesson Learned: The most significant lesson learned from past incidents was Multi-tenant cloud architectures require additional safeguards to prevent cross-user data leakage via hardware flaws.
Most Significant Recommendation Implemented: The most significant recommendation implemented to improve cybersecurity was Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) with behavioral analysis, Conduct regular penetration testing for internal applications, Expand bug bounty program to include web infrastructure with competitive rewards, Enforce code reviews for security-critical changes, Intel should release microcode/firmware patches to mitigate BPRC exploits., Eliminate hardcoded credentials; use secure secret management (e.g., HashiCorp Vault), Long-term: Redesign speculative execution mechanisms to eliminate side-channel risks without sacrificing performance., Conduct comprehensive audits of internal portals for hardcoded credentials and authentication flaws., Establish a dedicated channel for high-severity vulnerability disclosures, Regularly test for Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and similar access control vulnerabilities., Cloud providers should implement network segmentation and memory isolation techniques for shared hardware., American businesses should guard their networks against Iranian government-sponsored cyberattacks and 'low-level' digital intrusions by pro-Iran hacktivists., Implement comprehensive server-side validation for all authentication flows, Enhance communication protocols for vulnerability disclosures to ensure researchers feel acknowledged and valued., Organizations should monitor for unusual memory access patterns indicative of speculative execution attacks., Expand bug bounty program scope to include critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities., Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all internal systems and especially those handling sensitive data..
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident are US Homeland Security, Eaton Works Research (Vulnerability Disclosure), ETH Zurich’s Computer Security Group (COMSEC), Eaton Z (Security Researcher Blog Post), Morphisec, Twitter user 'freak' and TechRadar Pro.
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is Ongoing.
Most Recent Customer Advisory: The most recent customer advisory issued was an Intel and cloud providers should issue advisories warning customers of potential risks and mitigation steps.
Most Recent Entry Point: The most recent entry point used by an initial access broker were an Russian and Chinese darknet forums and X.
Most Significant Root Cause: The most significant root cause identified in post-incident analysis was State-sponsored cyber warfare and financial incentives, Over-reliance on client-side security controlsLack of secure coding practices (hardcoded credentials, weak encryption)Inadequate API security (unauthenticated token issuance, lack of input validation)Poor secret management (exposed GitHub PAT, API keys)Insufficient security testing for internal applications, Hardcoded credentials in multiple internal portals.Weak authentication mechanisms allowing bypass via manipulated login requests.Lack of proper access controls to restrict data exposure.Inadequate response to vulnerability disclosure, potentially discouraging future ethical reporting., Inherent security flaws in speculative execution implementations in Intel processors.Lack of hardware-level isolation between tenants in shared environments.Performance optimizations prioritized over security in CPU design..
Most Significant Corrective Action: The most significant corrective action taken based on post-incident analysis was Server-side validation enforcedHardcoded credentials removed/replaced with secure alternativesAPI security hardened (token validation, rate limiting)Encryption standards updatedBug bounty program review initiated, Patched vulnerable portals and removed hardcoded credentials.Presumably reviewed and strengthened authentication processes (though not explicitly detailed)..
.png)
FreePBX Endpoint Manager is a module for managing telephony endpoints in FreePBX systems. Versions prior to 16.0.96 and 17.0.1 through 17.0.9 have a weak default password. By default, this is a 6 digit numeric value which can be brute forced. (This is the app_password parameter). Depending on local configuration, this password could be the extension, voicemail, user manager, DPMA or EPM phone admin password. This issue is fixed in versions 16.0.96 and 17.0.10.
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. In versions 2.8.11 and below, the MySQLWriteTool executes arbitrary SQL provided by the caller using PDO::prepare() + execute() without semantic restrictions. This is consistent with the name (“write tool”), but in an LLM/agent context it becomes a high-risk capability: prompt injection or indirect prompt manipulation can cause execution of destructive queries such as DROP TABLE, TRUNCATE, DELETE, ALTER, or privilege-related statements (subject to DB permissions). Deployments that expose an agent with MySQLWriteTool enabled to untrusted input and/or run the tool with a DB user that has broad privileges are impacted. This issue is fixed in version 2.8.12.
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. Versions 2.8.11 and below use MySQLSelectTool, which is vulnerable to Read-Only Bypass. MySQLSelectTool is intended to be a read-only SQL tool (e.g., for LLM agent querying, however, validation based on the first keyword (e.g., SELECT) and a forbidden-keyword list does not block file-writing constructs such as INTO OUTFILE / INTO DUMPFILE. As a result, an attacker who can influence the tool input (e.g., via prompt injection through a public agent endpoint) may write arbitrary files to the DB server if the MySQL/MariaDB account has the FILE privilege and server configuration permits writes to a useful location (e.g., a web-accessible directory). This issue is fixed in version 2.8.12.
Okta Java Management SDK facilitates interactions with the Okta management API. In versions 11.0.0 through 20.0.0, race conditions may arise from concurrent requests using the ApiClient class. This could cause a status code or response header from one request’s response to influence another request’s response. This issue is fixed in version 20.0.1.
The Auth0 Next.js SDK is a library for implementing user authentication in Next.js applications. When using versions 4.11.0 through 4.11.2 and 4.12.0, simultaneous requests on the same client may result in improper lookups in the TokenRequestCache for the request results. This issue is fixed in versions 4.11.2 and 4.12.1.

Get company history
Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.
