Company Details
ibm
332,876
18,639,680
5415
ibm.com
0
IBM_3075085
In-progress

IBM Company CyberSecurity Posture
ibm.comWe don’t just imagine the future — we create it. We collaborate with technologists, developers and engineers to turn bold ideas into real-world impact. We partner with iconic brands like Ferrari and global events like the US Open, Wimbledon and The Masters to bring innovation to the world’s biggest stages and greatest fans. We work side-by-side with our clients, communities and even competitors to harness the power of AI, hybrid cloud and quantum computing — all to build a smarter, more efficient world. If you're fueled by curiosity and driven to make a difference, you'll feel right at home. Let’s create smarter business — together.
Company Details
ibm
332,876
18,639,680
5415
ibm.com
0
IBM_3075085
In-progress
Between 750 and 799

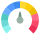 IBM Global Score (TPRM)
IBM Global Score (TPRM)XXXX

Description: The article highlights systemic vulnerabilities in IBM’s research, where organizations managing an average of **83 security tools from 29 vendors** face severe operational inefficiencies. Fragmented architectures—exemplified by IBM’s findings—create blind spots, with **95% of security leaders admitting redundant tools lack full integration**. This sprawl leads to **72-day delays in threat detection** and **84-day delays in containment**, directly enabling attackers to exploit gaps. The study underscores that **one-third of breaches originate from phishing**, with Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) failing to block an average of **67.5 phishing emails per 100 mailboxes monthly**. Default configurations, misaligned protections, and unintegrated tools amplify risks, resulting in **missed handoffs, poor detection, and inflated response costs**. The cumulative effect is **reputational damage, financial loss from prolonged breaches, and erosion of customer trust**, particularly for smaller teams lacking resources to maintain defenses. IBM’s own data reveals that non-consolidated environments suffer **101% lower ROI** compared to unified platforms, signaling systemic exposure to **sophisticated social engineering and evolving threat tactics** that bypass static defenses.
Description: The California Office of the Attorney General disclosed that IBM suffered an unauthorized access incident affecting the **Janssen CarePath platform**, a database containing personal information. The breach was reported on **September 22, 2023**, though the exact date of the intrusion remains undisclosed. While the specifics of the compromised data were not detailed in the report, the incident involved the exposure of personal information, likely belonging to customers or patients associated with the platform. Given the nature of Janssen CarePath—a service supporting healthcare-related financial and treatment assistance—the breach raises concerns about potential misuse of sensitive health or personally identifiable information (PII). IBM has not publicly confirmed the scale of the breach or whether the exposed data was exfiltrated, but the involvement of a government authority suggests regulatory scrutiny and possible compliance implications under data protection laws like **CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)** or **HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)** if health data was impacted.
Description: The article highlights IBM’s **2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report**, which underscores escalating financial and operational damages from breaches due to prolonged investigations, regulatory scrutiny, and unauthorized data exposure—including leaks via ungoverned AI tools or improper file sharing. The report aligns with broader trends cited by **ENISA (2024)**, noting persistent **ransomware and data theft** targeting sensitive corporate and customer data. These breaches exploit weak access controls, unclear permissions, and inadequate audit trails in virtual data rooms (VDRs), leading to **costly remediation, reputational harm, and compliance violations**. The financial impact is compounded by **delayed incident response**, where breaches involving high-value data (e.g., M&A documents, employee records, or customer PII) incur **higher cleanup costs** and **regulatory penalties**. The article implies that organizations using substandard VDRs face **increased risk of insider threats, third-party leaks, or ransomware attacks**, as demonstrated by real-world cases where **unauthorized AI processing or mass downloads** of sensitive files went undetected until post-breach forensics. The cumulative effect threatens **deal integrity, investor trust, and long-term business viability**, particularly in high-stakes sectors like finance, healthcare, or critical infrastructure.
Description: The IBM report highlights the escalating financial toll of data breaches in the healthcare industry, which consistently ranks as the most expensive sector for such incidents. Between May 2020 and February 2025, the average cost of a healthcare data breach surged to **$10.93 million USD**, the highest across all industries. These breaches often involve the exposure of highly sensitive patient records, including medical histories, treatment details, and personally identifiable information (PII). A typical incident in this sector may stem from a **cyber attack**—such as ransomware or targeted hacking—where threat actors exploit vulnerabilities in hospital IT systems or third-party vendors.The consequences extend beyond financial losses, disrupting critical healthcare services. For instance, a ransomware attack could encrypt patient databases, delaying emergency treatments, surgeries, or diagnostic procedures. In extreme cases, such disruptions have been linked to increased patient mortality rates. The breach’s ripple effects also erode public trust, trigger regulatory fines (e.g., HIPAA violations), and necessitate costly remediation efforts, including system overhauls and credit monitoring for affected individuals.Given the life-or-death stakes of healthcare data integrity, these breaches are classified among the most severe, often involving **criminal hackers** or state-sponsored groups targeting intellectual property (e.g., drug patents) or aiming to destabilize regional health infrastructure.
Description: The incident involves a **403 Forbidden** error, which typically indicates unauthorized access to a restricted resource on IBM’s systems. While the error message itself does not disclose specifics, such incidents can stem from misconfigured access controls, failed authentication attempts, or potential probing by malicious actors (e.g., cyber attackers testing for vulnerabilities). If this error resulted from an external attack—such as a **brute-force attempt, credential stuffing, or exploitation of an exposed API**—it could signal a **security weakness** in IBM’s web infrastructure. However, the provided details do not confirm data compromise, system breach, or operational disruption. The lack of further context (e.g., logs, incident reports) limits assessment to a **potential low-impact security event**, though it warrants investigation to rule out targeted reconnaissance or early-stage cyber threats.
Description: The incident involves a **403 Forbidden** error on an IBM web page, indicating unauthorized access or a misconfigured security restriction. While the error itself does not explicitly detail a cyberattack, it may suggest a potential **access control vulnerability** or an unintended exposure of internal systems. If exploited, such vulnerabilities could allow attackers to probe deeper into IBM’s infrastructure, potentially leading to data exposure or service disruptions. The incident reference number (18.561e1202.1762842001.646fd49b) implies internal tracking, but no public details confirm data breaches or operational impact. However, unaddressed access flaws could escalate into broader security risks, including credential stuffing, API abuses, or reconnaissance for targeted attacks. IBM’s global scale means even minor vulnerabilities could have cascading effects if left unresolved.
Description: The incident involves a **403 Forbidden** error, indicating unauthorized access to an IBM web resource (Incident ID: **18.ceb0f748.1757485191.4eafbe3**). While the error itself does not confirm a breach, it suggests a potential **misconfigured access control, exposed internal page, or failed security measure** that could allow attackers to probe for vulnerabilities. If exploited, this could lead to unauthorized data exposure, credential harvesting, or further system infiltration. The lack of public details implies IBM may have mitigated the issue internally, but the incident highlights risks of **improper access restrictions**, which are common entry points for cyber attacks. Without evidence of data theft or operational disruption, the impact remains speculative but warrants classification as a **security vulnerability** requiring remediation to prevent escalation.
Description: The incident involves a **403 Forbidden** error, indicating unauthorized or restricted access to an IBM web resource. While the error itself does not explicitly detail a cybersecurity breach, such errors can sometimes mask underlying security issues like misconfigured access controls, failed authentication attempts, or potential probing by malicious actors. If this error persists across critical systems or is part of a larger pattern (e.g., repeated unauthorized access attempts), it could signal a **vulnerability** in IBM’s web infrastructure—either an exposed endpoint, improper permission settings, or a precursor to a more severe attack (e.g., reconnaissance for a future breach). Without additional context, the direct impact remains unclear, but unauthorized access attempts or misconfigurations could lead to data exposure or system compromise if left unaddressed.
Description: Four zero-day vulnerabilities impacted an IBM security product after the company refused to patch bugs following a private bug disclosure attempt. The bugs impacted the IBM Data Risk Manager (IDRM). It is an enterprise security tool that aggregates feeds from vulnerability scanning tools and other risk management tools to let admins investigate security issues. The compromise of product led to a full-scale company compromise, as the tool had credentials to access other security tools. It contained information about critical vulnerabilities that affect the company.
Description: IBM experienced a cloud outage on Wednesday that lasted over four hours, causing users to be unable to access the console for managing their cloud resources or to open and view support cases. This outage repeated a similar incident from Tuesday. Additionally, IBM identified a critical-rated vulnerability in its QRadar threat detection and response tools and Cloud Pak for Security integration suite, which left a password in a configuration file. The vulnerability was scored 9.6 on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System, and IBM's security bulletin also advised of four other QRadar flaws.


IBM has 733.33% more incidents than the average of same-industry companies with at least one recorded incident.
IBM has 669.23% more incidents than the average of all companies with at least one recorded incident.
IBM reported 6 incidents this year: 0 cyber attacks, 0 ransomware, 5 vulnerabilities, 1 data breaches, compared to industry peers with at least 1 incident.
IBM cyber incidents detection timeline including parent company and subsidiaries

We don’t just imagine the future — we create it. We collaborate with technologists, developers and engineers to turn bold ideas into real-world impact. We partner with iconic brands like Ferrari and global events like the US Open, Wimbledon and The Masters to bring innovation to the world’s biggest stages and greatest fans. We work side-by-side with our clients, communities and even competitors to harness the power of AI, hybrid cloud and quantum computing — all to build a smarter, more efficient world. If you're fueled by curiosity and driven to make a difference, you'll feel right at home. Let’s create smarter business — together.


ASGN Incorporated (NYSE: ASGN) is a leading provider of IT services and solutions across the commercial and government sectors. ASGN helps corporate enterprises and government organizations develop, implement and operate critical IT and business solutions through its integrated offerings. For more i

We bring together the right people, the right technology and the right partners to create innovative solutions that make positive impact and address some of the most urgent and complex challenges facing the modern world. With a focus on serving governments globally, Serco’s services span justice,

A Stefanini é uma multinacional brasileira que atua no setor de serviços em TI. Com um suporte em mais de 30 idiomas, a Stefanini, 5ª empresa mais internacionalizada, segundo a Fundação Dom Cabral, atua em mais de 35 países e e está entre as 100 maiores empresas de TI do mundo (BBC News). Uma das ma

We’re TD SYNNEX (NYSE: SNX), a leading distributor and solutions aggregator for the IT ecosystem. We’re 23,000 of the IT industry’s best and brightest, who share an unwavering passion for bringing compelling technology products, services and solutions to the world. We’re an innovative partner that
FPT Software, a subsidiary of FPT Corporation, is a global technology and IT services provider headquartered in Vietnam, with USD 1.22 billion in revenue (2024) and over 33,000 employees in 30 countries. The company champions complex business opportunities and challenges with its world-class servic

TIVIT is a Brazil-based multinational company that offers enterprise-level digital solutions, and operates in ten countries in Latin America. We help our clients develop their businesses by offering industry-leading digital solutions divided into four main categories: Digital Business, Cloud Solutio
Coforge is a global digital services and solutions provider, that leverages emerging technologies and deep domain expertise to deliver real-world business impact for its clients. A focus on select industries, a deep domain understanding of the underlying processes of those industries and partners

In a rapidly changing world, technology is everything. It's in the fabric of society. In every part of every business. At the very heart of human evolution. It’s a great power that comes with great responsibility. At Tietoevry, we believe it’s time to shift perspective. It’s not about what technolo

Infosys BPM Ltd., the business process management subsidiary of Infosys Ltd. (NYSE: INFY), was set up in April 2002. Infosys BPM focuses on integrated end-to-end outsourcing and delivers transformational benefits to its clients through reduced costs, ongoing productivity improvements, and process re
.png)
Press release - HTF Market Intelligence Consulting Pvt. Ltd. - Digital Immune Market Is Going to Boom | Major Giants IBM, Microsoft,...
Learn more about our team of experts who closely monitor and assess cybersecurity trends and insights, including discovering and ethically...
Cyviz AS partners with IBM to upgrade the IBM X-Force Cyber Range in Cambridge, enhancing cybersecurity training with hands-on simulations...
Cyviz(CYVIZ.OL) said Friday it secured a deal to provide cyber range and training center services to IBM's X-Force Cyber Range in Cambridge,...
The programme will be delivered across India through a hybrid model, combining direct engagement with universities and collaboration with...
An update from Cyviz AS ( ($DE:8P9) ) is now available. Cyviz AS has entered into a new partner contract with IBM to modernize and upgrade...
After a recent AI-assisted cyber attack that was observed to be “90% autonomous”, many questions are being raised. IBM X-Force weighs in.
IBM released security updates addressing vulnerabilities in its AIX that could allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands.
IBM has released urgent security patches addressing four severe vulnerabilities in AIX and VIOS systems that enable remote attackers to...

Explore insights on cybersecurity incidents, risk posture, and Rankiteo's assessments.
The official website of IBM is http://www.ibm.com.
According to Rankiteo, IBM’s AI-generated cybersecurity score is 766, reflecting their Fair security posture.
According to Rankiteo, IBM currently holds 0 security badges, indicating that no recognized compliance certifications are currently verified for the organization.
According to Rankiteo, IBM is not certified under SOC 2 Type 1.
According to Rankiteo, IBM does not hold a SOC 2 Type 2 certification.
According to Rankiteo, IBM is not listed as GDPR compliant.
According to Rankiteo, IBM does not currently maintain PCI DSS compliance.
According to Rankiteo, IBM is not compliant with HIPAA regulations.
According to Rankiteo,IBM is not certified under ISO 27001, indicating the absence of a formally recognized information security management framework.
IBM operates primarily in the IT Services and IT Consulting industry.
IBM employs approximately 332,876 people worldwide.
IBM presently has no subsidiaries across any sectors.
IBM’s official LinkedIn profile has approximately 18,639,680 followers.
IBM is classified under the NAICS code 5415, which corresponds to Computer Systems Design and Related Services.
No, IBM does not have a profile on Crunchbase.
Yes, IBM maintains an official LinkedIn profile, which is actively utilized for branding and talent engagement, which can be accessed here: https://www.linkedin.com/company/ibm.
As of December 11, 2025, Rankiteo reports that IBM has experienced 10 cybersecurity incidents.
IBM has an estimated 37,490 peer or competitor companies worldwide.
Incident Types: The types of cybersecurity incidents that have occurred include Vulnerability, Breach and Cyber Attack.
Total Financial Loss: The total financial loss from these incidents is estimated to be $2.02 thousand.
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through an remediation measures with health checks of resources and contacting ibm cloud support, and communication strategy with messages sent to customers and apology issued by ibm japan, and remediation measures with replatforming (consolidating security tools), remediation measures with api-centric tool integration, remediation measures with adaptive capabilities (ml/behavioral analysis), remediation measures with automation for shared threat intelligence, and communication strategy with expert insights (techradar pro article), communication strategy with awareness of tool sprawl risks, and enhanced monitoring with continuous roi measurement (time-to-detect/respond), and remediation measures with verify url correctness, remediation measures with check access permissions, remediation measures with review waf/acl rules, remediation measures with clear cache/cookies, and recovery measures with restore access via correct credentials/permissions, recovery measures with update security policies if misconfigured, and communication strategy with reported to california office of the attorney general, and remediation measures with verify url correctness, remediation measures with check case sensitivity, remediation measures with review access permissions, remediation measures with inspect waf/acl rules if internal, and recovery measures with redirect users to ibm homepage, recovery measures with provide alternative contact methods for support, and containment measures with sso with mfa, containment measures with ip allow/deny lists, containment measures with session timeouts, containment measures with device checks, containment measures with granular role-based permissions, containment measures with document watermarking, containment measures with print/download controls, containment measures with copy-paste suppression, containment measures with browser-only viewers, containment measures with built-in redaction, containment measures with drm for files, containment measures with ai boundaries, and remediation measures with tamper-evident audit logs, remediation measures with anomaly detection alerts, remediation measures with region-pinned data storage, remediation measures with third-party security certifications, and recovery measures with backup restoration protocols, recovery measures with self-contained audit archives, and enhanced monitoring with user activity analytics, enhanced monitoring with behavioral anomaly flags (e.g., rapid page views, mass downloads), and remediation measures with suggested actions provided to users: verify url spelling, check case sensitivity, or navigate from the ibm homepage., and remediation measures with verify url correctness, remediation measures with check access permissions, remediation measures with review waf/acl rules, remediation measures with clear cache/cookies, and recovery measures with restore access via it support, recovery measures with update security policies if misconfigured..
Title: IBM Data Risk Manager Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Description: Four zero-day vulnerabilities impacted the IBM Data Risk Manager (IDRM) after the company refused to patch bugs following a private bug disclosure attempt. The compromise of the product led to a full-scale company compromise, as the tool had credentials to access other security tools.
Type: Zero-Day Exploit
Attack Vector: Unpatched Vulnerability
Vulnerability Exploited: Four zero-day vulnerabilities in IBM Data Risk Manager
Title: IBM Cloud Outage and Critical Vulnerability
Description: IBM experienced a cloud outage and a critical-rated vulnerability in its QRadar threat detection and response tools and Cloud Pak for Security integration suite.
Date Detected: 2023-05-21
Date Resolved: 2023-05-21
Type: Outage and Vulnerability
Vulnerability Exploited: CVE-2025-2502
Title: Security Architecture Bloat and Fragmentation Leading to Increased Cybersecurity Risks
Description: The average organization now manages 83 security tools from 29 vendors, leading to rising complexity, tool sprawl, and mounting pressure on security teams. This fragmentation creates blind spots, slower threat detection (72 days longer), and weaker response times (84 days longer to contain threats), making it easier for attackers to exploit gaps. Traditional tools like Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) fail to block modern phishing attacks, with an average of 67.5 phishing emails evading SEGs per 100 mailboxes monthly. Smaller organizations are disproportionately affected, facing 7.5× more missed attacks than larger counterparts due to understaffing and misconfigured tools. Attack vectors include phishing (1/3 of breaches per Verizon DBIR), vendor scams, credential theft, and image-based phishing, which bypass static filtering and signature-based detection.
Date Publicly Disclosed: 2023-10-04T00:00:00Z
Type: Operational Risk
Attack Vector: Phishing (Email)Vendor ScamsCredential TheftImage-Based PhishingSocial Engineering
Vulnerability Exploited: Fragmented Security Tool IntegrationDefault Configurations in Security ToolsLack of API-Centric Threat Intelligence SharingStatic Filtering in SEGsSignature-Based Detection Gaps
Title: None
Description: IBM's report on the average cost of a data breach worldwide from May 2020 to February 2025, segmented by industry. The data highlights financial impacts across various sectors, emphasizing the escalating costs associated with cyber incidents over time.
Date Publicly Disclosed: 2025-08-12
Type: Data Breach Cost Analysis
Title: None
Description: A 403 Forbidden error was encountered when attempting to access an IBM page. Incident Number: 18.ceb0f748.1757485191.4eafbe3. The page could not be displayed, possibly due to access restrictions, misconfigured permissions, or a security measure (e.g., WAF blocking, IP restriction, or authentication failure).
Type: access_denial
Title: None
Description: A 403 Forbidden error was encountered when attempting to access an IBM page. Incident Number: 18.561e1202.1761373223.528ac1d8. The page could not be displayed, possibly due to access restrictions, misconfigured permissions, or a security measure (e.g., WAF blocking).
Type: access_denial
Title: None
Description: The article discusses the rising importance of secure virtual data room (VDR) software in 2025 due to increasing data breach costs, regulatory scrutiny, and sophisticated cyber threats like ransomware and data theft. It highlights the need for robust security features in VDRs, including identity management, granular permissions, document controls, Q&A safeguards, anomaly detection, tamper-evident audit trails, data residency compliance, and secure AI integration. The context implies heightened risks in high-stakes dealmaking (M&A, financings, audits) where unsecured data rooms could expose sensitive information to breaches, leaks, or unauthorized AI processing. IBM’s 2024 *Cost of a Data Breach* and ENISA’s 2024 threat reports are cited as evidence of escalating cyber risks, emphasizing the financial and operational impacts of inadequate data protection.
Type: Data Breach Risk
Vulnerability Exploited: Loose Sharing PermissionsUncontrolled AI Tool IntegrationInadequate Access ControlsLack of Anomaly DetectionPoor Data Residency Enforcement
Title: None
Description: A 403 Forbidden error was encountered when attempting to access an IBM page. Incident Number: 18.561e1202.1762842001.646fd49b. The page could not be displayed, possibly due to access restrictions, misconfigured permissions, or a security measure (e.g., WAF blocking, IP restriction, or authentication failure).
Type: access_denial
Common Attack Types: The most common types of attacks the company has faced is Vulnerability.
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through Phishing emails (1/3 of breaches)Vendor impersonationCredential theft.

Data Compromised: Critical vulnerability information
Systems Affected: IBM Data Risk ManagerOther security tools
Operational Impact: Full-scale company compromise

Systems Affected: IBM Cloud ConsoleSupport Cases
Downtime: ['2023-05-21 09:03 AM UTC', '2023-05-21 01:20 PM UTC']
Operational Impact: Users unable to access cloud resources and support cases
Brand Reputation Impact: Apologies issued by IBM Japan

Systems Affected: Email Systems (SEGs)Endpoint SecurityIdentity Management
Operational Impact: 72-day longer threat detection84-day longer threat containmentIncreased operational risk due to tool sprawlStretched security teamsHigher response costs
Brand Reputation Impact: Reputational damage due to delayed breach detection/responsePerceived insecurity by customers/partners
Identity Theft Risk: ['Credential theft via phishing']


Systems Affected: unspecified_IBM_web_page
Downtime: temporary (until access is restored or issue is resolved)
Operational Impact: minor (limited to inability to access a specific page)
Brand Reputation Impact: low (unless part of a larger outage or targeted attack)

Systems Affected: unspecified_IBM_web_page
Downtime: temporary (until access is restored or permissions corrected)
Operational Impact: minor (limited to inability to access a specific page)
Brand Reputation Impact: low (unless part of a broader outage or misconfiguration trend)

Financial Loss: Potential high costs due to prolonged breach investigations, regulatory fines, and cleanup (cited from IBM’s 2024 *Cost of a Data Breach*).
Systems Affected: Virtual Data Rooms (VDRs)Sensitive Deal DocumentsAI Processing Tools
Operational Impact: Slowed dealmaking processes due to heightened scrutiny, manual reviews, and distrust in insecure VDRs.
Brand Reputation Impact: Risk of reputational damage if breaches occur due to inadequate VDR security, leading to loss of trust in dealmaking partners.
Legal Liabilities: Potential violations of data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR) due to uncontrolled data transfers or leaks.

Systems Affected: IBM webpage (unspecified)
Downtime: temporary (until access is restored or issue is resolved)
Operational Impact: minor (limited to inability to access a specific page)
Brand Reputation Impact: low (unless recurrent or part of a larger pattern)
Average Financial Loss: The average financial loss per incident is $202.40.
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are Credentials (Via Phishing), Potential Pii (If Phishing Successful), , Personal Information, , Sensitive Deal Documents, Pii (Potential), Financial Records, Legal Contracts and .

Entity Name: IBM
Entity Type: Corporation
Industry: Technology
Location: Global
Size: Large

Entity Name: Average Organization (Generalized)
Entity Type: Enterprise, SME
Industry: Cross-Industry
Location: Global
Size: ['Small (higher risk)', 'Medium', 'Large']

Entity Name: IBM (Report Publisher)
Entity Type: Organization
Industry: Technology/IT Services
Location: Global
Size: Large (350,000+ employees)

Entity Name: IBM
Entity Type: corporation
Industry: technology
Location: global (HQ: Armonk, New York, USA)
Size: large

Entity Name: IBM
Entity Type: corporation
Industry: technology
Location: global (HQ: Armonk, New York, USA)
Size: large (350,000+ employees)

Entity Name: IBM
Entity Type: corporation
Industry: technology
Location: global (HQ: Armonk, New York, USA)
Size: large

Remediation Measures: Health checks of resources and contacting IBM Cloud Support
Communication Strategy: Messages sent to customers and apology issued by IBM Japan

Remediation Measures: Replatforming (consolidating security tools)API-centric tool integrationAdaptive capabilities (ML/behavioral analysis)Automation for shared threat intelligence
Communication Strategy: Expert Insights (TechRadar Pro article)Awareness of tool sprawl risks
Enhanced Monitoring: Continuous ROI measurement (time-to-detect/respond)

Remediation Measures: verify URL correctnesscheck access permissionsreview WAF/ACL rulesclear cache/cookies
Recovery Measures: restore access via correct credentials/permissionsupdate security policies if misconfigured

Remediation Measures: verify URL correctnesscheck case sensitivityreview access permissionsinspect WAF/ACL rules if internal
Recovery Measures: redirect users to IBM homepageprovide alternative contact methods for support

Containment Measures: SSO with MFAIP Allow/Deny ListsSession TimeoutsDevice ChecksGranular Role-Based PermissionsDocument WatermarkingPrint/Download ControlsCopy-Paste SuppressionBrowser-Only ViewersBuilt-In RedactionDRM for FilesAI Boundaries
Remediation Measures: Tamper-Evident Audit LogsAnomaly Detection AlertsRegion-Pinned Data StorageThird-Party Security Certifications
Recovery Measures: Backup Restoration ProtocolsSelf-Contained Audit Archives
Enhanced Monitoring: User Activity AnalyticsBehavioral Anomaly Flags (e.g., rapid page views, mass downloads)

Remediation Measures: verify URL correctnesscheck access permissionsreview WAF/ACL rulesclear cache/cookies
Recovery Measures: restore access via IT supportupdate security policies if misconfigured

Type of Data Compromised: Credentials (via phishing), Potential pii (if phishing successful)
Sensitivity of Data: High (credentials)Medium (corporate email access)
Personally Identifiable Information: Potential (if phishing leads to account takeover)

Type of Data Compromised: Sensitive deal documents, Pii (potential), Financial records, Legal contracts
Sensitivity of Data: High (M&A, financings, audits, board matters)
Data Exfiltration: Risk highlighted due to loose permissions and unapproved AI tool usage.
File Types Exposed: PDFOffice DocumentsMedia Files
Personally Identifiable Information: Potential (if PII is stored in VDRs without proper controls).
Prevention of Data Exfiltration: The company takes the following measures to prevent data exfiltration: Health checks of resources and contacting IBM Cloud Support, Replatforming (consolidating security tools), API-centric tool integration, Adaptive capabilities (ML/behavioral analysis), Automation for shared threat intelligence, , verify URL correctness, check access permissions, review WAF/ACL rules, clear cache/cookies, , verify URL correctness, check case sensitivity, review access permissions, inspect WAF/ACL rules if internal, , Tamper-Evident Audit Logs, Anomaly Detection Alerts, Region-Pinned Data Storage, Third-Party Security Certifications, , Suggested actions provided to users: verify URL spelling, check case sensitivity, or navigate from the IBM homepage., verify URL correctness, check access permissions, review WAF/ACL rules, clear cache/cookies, .
Handling of PII Incidents: The company handles incidents involving personally identifiable information (PII) through by sso with mfa, ip allow/deny lists, session timeouts, device checks, granular role-based permissions, document watermarking, print/download controls, copy-paste suppression, browser-only viewers, built-in redaction, drm for files, ai boundaries and .
Data Recovery from Ransomware: The company recovers data encrypted by ransomware through restore access via correct credentials/permissions, update security policies if misconfigured, , redirect users to IBM homepage, provide alternative contact methods for support, , Backup Restoration Protocols, Self-Contained Audit Archives, , restore access via IT support, update security policies if misconfigured, .

Regulations Violated: Potential GDPR (Europe), Data Protection Laws (Cross-Border Transfers),

Lessons Learned: Tool sprawl (83 tools from 29 vendors) increases complexity and risk, with 95% of leaders reporting redundant, unintegrated tools., Fragmentation leads to 72-day longer detection and 84-day longer containment, inflating costs and reputational damage., SEGs fail to block modern phishing (67.5 emails/month evade detection per 100 mailboxes), especially in understaffed SMEs., Default configurations and unintegrated tools create exploitable blind spots., AI/automation widens gaps when layered on disjointed architectures.

Lessons Learned: The report underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures across industries, with costs rising annually. Proactive investments in prevention, detection, and response capabilities are essential to mitigate financial and operational risks.

Lessons Learned: Insecure VDRs expose organizations to financial, operational, and reputational risks during high-stakes dealmaking. Proactive security measures (e.g., granular permissions, audit trails, AI governance) are critical to mitigating breaches and ensuring regulatory compliance.

Recommendations: Perform health checks of resources and contact IBM Cloud Support if issues persist

Recommendations: Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience.Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience.Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience.Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience.Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience.Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience.

Recommendations: Implement industry-specific cybersecurity frameworks tailored to high-risk sectors (e.g., healthcare, financial services)., Conduct regular cost-benefit analyses of security investments versus potential breach costs., Enhance employee training and incident response preparedness to reduce breach lifecycle durations., Leverage AI and automation for threat detection and response to lower average breach costs.Implement industry-specific cybersecurity frameworks tailored to high-risk sectors (e.g., healthcare, financial services)., Conduct regular cost-benefit analyses of security investments versus potential breach costs., Enhance employee training and incident response preparedness to reduce breach lifecycle durations., Leverage AI and automation for threat detection and response to lower average breach costs.Implement industry-specific cybersecurity frameworks tailored to high-risk sectors (e.g., healthcare, financial services)., Conduct regular cost-benefit analyses of security investments versus potential breach costs., Enhance employee training and incident response preparedness to reduce breach lifecycle durations., Leverage AI and automation for threat detection and response to lower average breach costs.Implement industry-specific cybersecurity frameworks tailored to high-risk sectors (e.g., healthcare, financial services)., Conduct regular cost-benefit analyses of security investments versus potential breach costs., Enhance employee training and incident response preparedness to reduce breach lifecycle durations., Leverage AI and automation for threat detection and response to lower average breach costs.

Recommendations: Investigate whether the 403 error is due to a misconfiguration or a deliberate security block (e.g., DDoS protection, IP blacklisting)., Ensure web application firewalls (WAFs) and access control lists (ACLs) are properly tuned to avoid false positives., Monitor for patterns of unauthorized access attempts that may trigger such errors., Provide clear user guidance for troubleshooting 403 errors (e.g., checking URL typos, permissions, or VPN requirements).Investigate whether the 403 error is due to a misconfiguration or a deliberate security block (e.g., DDoS protection, IP blacklisting)., Ensure web application firewalls (WAFs) and access control lists (ACLs) are properly tuned to avoid false positives., Monitor for patterns of unauthorized access attempts that may trigger such errors., Provide clear user guidance for troubleshooting 403 errors (e.g., checking URL typos, permissions, or VPN requirements).Investigate whether the 403 error is due to a misconfiguration or a deliberate security block (e.g., DDoS protection, IP blacklisting)., Ensure web application firewalls (WAFs) and access control lists (ACLs) are properly tuned to avoid false positives., Monitor for patterns of unauthorized access attempts that may trigger such errors., Provide clear user guidance for troubleshooting 403 errors (e.g., checking URL typos, permissions, or VPN requirements).Investigate whether the 403 error is due to a misconfiguration or a deliberate security block (e.g., DDoS protection, IP blacklisting)., Ensure web application firewalls (WAFs) and access control lists (ACLs) are properly tuned to avoid false positives., Monitor for patterns of unauthorized access attempts that may trigger such errors., Provide clear user guidance for troubleshooting 403 errors (e.g., checking URL typos, permissions, or VPN requirements).

Recommendations: Audit web server access controls and WAF rules to prevent false positives., Implement user-friendly error pages with troubleshooting guidance., Monitor for patterns of 403 errors that may indicate targeted scanning or misconfigurations.Audit web server access controls and WAF rules to prevent false positives., Implement user-friendly error pages with troubleshooting guidance., Monitor for patterns of 403 errors that may indicate targeted scanning or misconfigurations.Audit web server access controls and WAF rules to prevent false positives., Implement user-friendly error pages with troubleshooting guidance., Monitor for patterns of 403 errors that may indicate targeted scanning or misconfigurations.

Recommendations: Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications.

Recommendations: Implement proper error handling for 403 pages to avoid confusion with security incidents., Review access control lists (ACLs) and web application firewall (WAF) rules to prevent false positives., Ensure clear communication channels for users encountering access issues.Implement proper error handling for 403 pages to avoid confusion with security incidents., Review access control lists (ACLs) and web application firewall (WAF) rules to prevent false positives., Ensure clear communication channels for users encountering access issues.Implement proper error handling for 403 pages to avoid confusion with security incidents., Review access control lists (ACLs) and web application firewall (WAF) rules to prevent false positives., Ensure clear communication channels for users encountering access issues.
Key Lessons Learned: The key lessons learned from past incidents are Tool sprawl (83 tools from 29 vendors) increases complexity and risk, with 95% of leaders reporting redundant, unintegrated tools.,Fragmentation leads to 72-day longer detection and 84-day longer containment, inflating costs and reputational damage.,SEGs fail to block modern phishing (67.5 emails/month evade detection per 100 mailboxes), especially in understaffed SMEs.,Default configurations and unintegrated tools create exploitable blind spots.,AI/automation widens gaps when layered on disjointed architectures.The report underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures across industries, with costs rising annually. Proactive investments in prevention, detection, and response capabilities are essential to mitigate financial and operational risks.Insecure VDRs expose organizations to financial, operational, and reputational risks during high-stakes dealmaking. Proactive security measures (e.g., granular permissions, audit trails, AI governance) are critical to mitigating breaches and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Implemented Recommendations: The company has implemented the following recommendations to improve cybersecurity: Perform health checks of resources and contact IBM Cloud Support if issues persist.

Source: IBM Security Bulletin

Source: IBM and Palo Alto Networks Study

Source: Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR)

Source: TechRadar Pro Expert Insights (Eyal Benishti, IRONSCALES)
URL: https://www.techradar.com/news/submit-your-story-to-techradar-pro
Date Accessed: 2023-10-04

Source: Statista
URL: https://www.statista.com/statistics/387861/cost-data-breach-by-industry/
Date Accessed: 2025-09-04

Source: IBM Error Page

Source: IBM Error Page

Source: IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report

Source: ENISA’s 2024 Threat Landscape Report

Source: IBM Error Page
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at and Source: IBM Security Bulletin, and Source: IBM and Palo Alto Networks Study, and Source: Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), and Source: TechRadar Pro Expert Insights (Eyal Benishti, IRONSCALES)Url: https://www.techradar.com/news/submit-your-story-to-techradar-proDate Accessed: 2023-10-04, and Source: StatistaUrl: https://www.statista.com/statistics/387861/cost-data-breach-by-industry/Date Accessed: 2025-09-04, and Source: IBM Error Page, and Source: California Office of the Attorney GeneralDate Accessed: 2023-09-22, and Source: IBM Error Page, and Source: IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, and Source: ENISA’s 2024 Threat Landscape Report, and Source: IBM Error Page, and Source: IBM Error Page.

Investigation Status: Ongoing (Industry-Wide Analysis)

Investigation Status: Completed (Report Published)

Investigation Status: unconfirmed (could be benign or indicative of a security event)

Investigation Status: unconfirmed (could be benign access issue or security-related)

Investigation Status: unconfirmed (could be a false positive or legitimate access restriction)
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through Messages sent to customers and apology issued by IBM Japan, Expert Insights (Techradar Pro Article), Awareness Of Tool Sprawl Risks and Reported to California Office of the Attorney General.

Customer Advisories: Perform health checks of their resources and contact IBM Cloud Support if they continue to experience failures.

Stakeholder Advisories: Security Leaders Urged To Replatform And Consolidate Tools To Reduce Risk..
Customer Advisories: Organizations advised to assess email security gaps (SEGs) and adopt adaptive defenses.

Customer Advisories: Organizations are advised to evaluate VDR software based on security features that align with high-stakes dealmaking requirements, prioritizing governance, auditability, and risk mitigation.
Advisories Provided: The company provides the following advisories to stakeholders and customers following an incident: were Perform health checks of their resources and contact IBM Cloud Support if they continue to experience failures., Security Leaders Urged To Replatform And Consolidate Tools To Reduce Risk., Organizations Advised To Assess Email Security Gaps (Segs) And Adopt Adaptive Defenses., , Organizations are advised to evaluate VDR software based on security features that align with high-stakes dealmaking requirements, prioritizing governance, auditability, and risk mitigation. and Users were advised to check URL spelling or start from the IBM homepage..

Entry Point: Phishing Emails (1/3 Of Breaches), Vendor Impersonation, Credential Theft,
High Value Targets: Email Accounts, Corporate Credentials, Financial Systems,
Data Sold on Dark Web: Email Accounts, Corporate Credentials, Financial Systems,

High Value Targets: M&A Documents, Financial Records, Board Materials,
Data Sold on Dark Web: M&A Documents, Financial Records, Board Materials,

Root Causes: Over-Reliance On Bolt-On Security Tools Without Integration., Lack Of Api-Centric Threat Intelligence Sharing., Static Detection Methods (Segs) Unable To Counter Social Engineering., Understaffed Teams Unable To Maintain Tool Configurations., Default Settings And Unintegrated Tools Creating Blind Spots.,
Corrective Actions: Transition To Unified Cybersecurity Platforms (101% Roi)., Replace Segs With Api-Based, Adaptive Email Security., Automate Threat Intelligence Sharing Across Tools., Continuous Tuning Of Security Tools To Address Evolving Tactics., Prioritize Domains With Highest Threat Volume (E.G., Email).,

Root Causes: Increasing Sophistication Of Cyber Threats., Expanding Attack Surfaces (E.G., Cloud Migration, Remote Work)., Regulatory Complexities And Compliance Costs., Shortage Of Skilled Cybersecurity Professionals.,

Root Causes: Inadequate Access Controls, Lack Of Activity Monitoring, Unsecured Data Sharing, Poor Data Residency Management, Unrestricted Ai Tool Integration,
Corrective Actions: Adopt Vdrs With Governed Workspaces And Predictive Security Controls., Enforce Least-Privilege Access And Just-In-Time Permissions., Implement Real-Time Anomaly Detection And Automated Containment., Ensure Tamper-Proof Audit Trails For Compliance And Dispute Resolution., Restrict Cross-Border Data Transfers To Compliant Storage Regions.,

Root Causes: Potential Waf/Acl Misconfiguration, Incorrect Url Input, Session/Cookie Expiration, Ip-Based Restriction,
Corrective Actions: Audit Security Rules, Improve User Guidance For Errors, Log And Monitor 403 Events For Anomalies,
Post-Incident Analysis Process: The company's process for conducting post-incident analysis is described as Continuous Roi Measurement (Time-To-Detect/Respond), , User Activity Analytics, Behavioral Anomaly Flags (E.G., Rapid Page Views, Mass Downloads), .
Corrective Actions Taken: The company has taken the following corrective actions based on post-incident analysis: Transition To Unified Cybersecurity Platforms (101% Roi)., Replace Segs With Api-Based, Adaptive Email Security., Automate Threat Intelligence Sharing Across Tools., Continuous Tuning Of Security Tools To Address Evolving Tactics., Prioritize Domains With Highest Threat Volume (E.G., Email)., , Adopt Vdrs With Governed Workspaces And Predictive Security Controls., Enforce Least-Privilege Access And Just-In-Time Permissions., Implement Real-Time Anomaly Detection And Automated Containment., Ensure Tamper-Proof Audit Trails For Compliance And Dispute Resolution., Restrict Cross-Border Data Transfers To Compliant Storage Regions., , Audit Security Rules, Improve User Guidance For Errors, Log And Monitor 403 Events For Anomalies, .
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on 2023-05-21.
Most Recent Incident Publicly Disclosed: The most recent incident publicly disclosed was on 2023-09-22.
Most Recent Incident Resolved: The most recent incident resolved was on 2023-05-21.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident were Critical vulnerability information, , Personal Information and .
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident was IBM Data Risk ManagerOther security tools and IBM Cloud ConsoleSupport Cases and Email Systems (SEGs)Endpoint SecurityIdentity Management and unspecified_IBM_web_page and Janssen CarePath platform database and unspecified_IBM_web_page and Virtual Data Rooms (VDRs)Sensitive Deal DocumentsAI Processing Tools and Potential IBM web page or service (unconfirmed) and IBM webpage (unspecified).
Containment Measures in Most Recent Incident: The containment measures taken in the most recent incident was SSO with MFAIP Allow/Deny ListsSession TimeoutsDevice ChecksGranular Role-Based PermissionsDocument WatermarkingPrint/Download ControlsCopy-Paste SuppressionBrowser-Only ViewersBuilt-In RedactionDRM for FilesAI Boundaries.
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach were Critical vulnerability information and Personal Information.
Most Significant Lesson Learned: The most significant lesson learned from past incidents was AI/automation widens gaps when layered on disjointed architectures., The report underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures across industries, with costs rising annually. Proactive investments in prevention, detection, and response capabilities are essential to mitigate financial and operational risks., Insecure VDRs expose organizations to financial, operational, and reputational risks during high-stakes dealmaking. Proactive security measures (e.g., granular permissions, audit trails, AI governance) are critical to mitigating breaches and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Most Significant Recommendation Implemented: The most significant recommendation implemented to improve cybersecurity was Audit web server access controls and WAF rules to prevent false positives., Prioritize adaptive tools: Use ML, behavioral analysis, and human feedback to counter evolving threats., Perform health checks of resources and contact IBM Cloud Support if issues persist, Implement industry-specific cybersecurity frameworks tailored to high-risk sectors (e.g., healthcare, financial services)., Monitor for patterns of 403 errors that may indicate targeted scanning or misconfigurations., Avoid 'more tools' mindset: Simplify to reduce operational burden and improve resilience., Deploy anomaly detection for unusual access patterns (e.g., off-hour activity)., Pin data storage to specific regions and document sub-processors., Implement user-friendly error pages with troubleshooting guidance., Implement proper error handling for 403 pages to avoid confusion with security incidents., Restrict AI tool usage to governed environments with disable options., Replatform: Consolidate tools into a unified, API-centric architecture with shared intelligence and automation., Enforce role-based permissions with inheritance and reversible exceptions., Test security controls regularly (e.g., simulated breach attempts)., Maintain tamper-evident, exportable audit logs with comprehensive metadata., Monitor for patterns of unauthorized access attempts that may trigger such errors., Enhance employee training and incident response preparedness to reduce breach lifecycle durations., Assess current stack: Inventory tools for overlap, integration gaps, and misconfigurations., Verify URL accuracy and case sensitivity when accessing IBM pages., Measure ROI: Track time-to-detect/respond to justify consolidation (101% ROI for platformized vs. 28% for fragmented)., Monitor for patterns of unauthorized access attempts (if this is part of a broader issue)., Investigate whether the 403 error is due to a misconfiguration or a deliberate security block (e.g., DDoS protection, IP blacklisting)., Use the IBM homepage as a starting point for navigation if access issues persist., Conduct regular cost-benefit analyses of security investments versus potential breach costs., Ensure clear communication channels for users encountering access issues., Use document controls (watermarks, DRM, redaction, screenshot deterrents)., Select VDR vendors with third-party security certifications., Provide clear user guidance for troubleshooting 403 errors (e.g., checking URL typos, permissions, or VPN requirements)., Ensure web application firewalls (WAFs) and access control lists (ACLs) are properly tuned to avoid false positives., Implement SSO with MFA and just-in-time user provisioning., Start small: Focus on high-risk domains (e.g., email, endpoint, identity) before expanding., Review access control lists (ACLs) and web application firewall (WAF) rules to prevent false positives., Route Q&A through approval workflows for sensitive disclosures. and Leverage AI and automation for threat detection and response to lower average breach costs..
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident are TechRadar Pro Expert Insights (Eyal Benishti, IRONSCALES), Statista, ENISA’s 2024 Threat Landscape Report, Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), IBM Error Page, IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, IBM and Palo Alto Networks Study, California Office of the Attorney General and IBM Security Bulletin.
Most Recent URL for Additional Resources: The most recent URL for additional resources on cybersecurity best practices is https://www.techradar.com/news/submit-your-story-to-techradar-pro, https://www.statista.com/statistics/387861/cost-data-breach-by-industry/ .
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is Ongoing (Industry-Wide Analysis).
Most Recent Stakeholder Advisory: The most recent stakeholder advisory issued was Security leaders urged to replatform and consolidate tools to reduce risk., .
Most Recent Customer Advisory: The most recent customer advisory issued were an Perform health checks of their resources and contact IBM Cloud Support if they continue to experience failures., Organizations advised to assess email security gaps (SEGs) and adopt adaptive defenses., Organizations are advised to evaluate VDR software based on security features that align with high-stakes dealmaking requirements, prioritizing governance, auditability, and risk mitigation. and Users were advised to check URL spelling or start from the IBM homepage.
Most Significant Root Cause: The most significant root cause identified in post-incident analysis was Over-reliance on bolt-on security tools without integration.Lack of API-centric threat intelligence sharing.Static detection methods (SEGs) unable to counter social engineering.Understaffed teams unable to maintain tool configurations.Default settings and unintegrated tools creating blind spots., Increasing sophistication of cyber threats.Expanding attack surfaces (e.g., cloud migration, remote work).Regulatory complexities and compliance costs.Shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals., Inadequate Access ControlsLack of Activity MonitoringUnsecured Data SharingPoor Data Residency ManagementUnrestricted AI Tool Integration, Possible misconfigured access permissions for the specific page.User error (e.g., incorrect URL or case sensitivity).Temporary access restriction (e.g., maintenance or IP blocking)., potential WAF/ACL misconfigurationincorrect URL inputsession/cookie expirationIP-based restriction.
Most Significant Corrective Action: The most significant corrective action taken based on post-incident analysis was Transition to unified cybersecurity platforms (101% ROI).Replace SEGs with API-based, adaptive email security.Automate threat intelligence sharing across tools.Continuous tuning of security tools to address evolving tactics.Prioritize domains with highest threat volume (e.g., email)., Adopt VDRs with governed workspaces and predictive security controls.Enforce least-privilege access and just-in-time permissions.Implement real-time anomaly detection and automated containment.Ensure tamper-proof audit trails for compliance and dispute resolution.Restrict cross-border data transfers to compliant storage regions., audit security rulesimprove user guidance for errorslog and monitor 403 events for anomalies.
.png)
FreePBX Endpoint Manager is a module for managing telephony endpoints in FreePBX systems. Versions prior to 16.0.96 and 17.0.1 through 17.0.9 have a weak default password. By default, this is a 6 digit numeric value which can be brute forced. (This is the app_password parameter). Depending on local configuration, this password could be the extension, voicemail, user manager, DPMA or EPM phone admin password. This issue is fixed in versions 16.0.96 and 17.0.10.
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. In versions 2.8.11 and below, the MySQLWriteTool executes arbitrary SQL provided by the caller using PDO::prepare() + execute() without semantic restrictions. This is consistent with the name (“write tool”), but in an LLM/agent context it becomes a high-risk capability: prompt injection or indirect prompt manipulation can cause execution of destructive queries such as DROP TABLE, TRUNCATE, DELETE, ALTER, or privilege-related statements (subject to DB permissions). Deployments that expose an agent with MySQLWriteTool enabled to untrusted input and/or run the tool with a DB user that has broad privileges are impacted. This issue is fixed in version 2.8.12.
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. Versions 2.8.11 and below use MySQLSelectTool, which is vulnerable to Read-Only Bypass. MySQLSelectTool is intended to be a read-only SQL tool (e.g., for LLM agent querying, however, validation based on the first keyword (e.g., SELECT) and a forbidden-keyword list does not block file-writing constructs such as INTO OUTFILE / INTO DUMPFILE. As a result, an attacker who can influence the tool input (e.g., via prompt injection through a public agent endpoint) may write arbitrary files to the DB server if the MySQL/MariaDB account has the FILE privilege and server configuration permits writes to a useful location (e.g., a web-accessible directory). This issue is fixed in version 2.8.12.
Okta Java Management SDK facilitates interactions with the Okta management API. In versions 11.0.0 through 20.0.0, race conditions may arise from concurrent requests using the ApiClient class. This could cause a status code or response header from one request’s response to influence another request’s response. This issue is fixed in version 20.0.1.
The Auth0 Next.js SDK is a library for implementing user authentication in Next.js applications. When using versions 4.11.0 through 4.11.2 and 4.12.0, simultaneous requests on the same client may result in improper lookups in the TokenRequestCache for the request results. This issue is fixed in versions 4.11.2 and 4.12.1.

Get company history
Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.
